Read on as we explain:
- What Are Ketones?
- Ketone Salts vs. Ketone Esters
- Why Use Exogenous Ketones?
- How Exogenous Ketones Work
- Future Applications & Research
- Further Reading & Recommended Resources
- Summary: The Takeaways
What Are Ketones?
Ketones are fuel for energy-generating mitochondria. Mitochondria are the power house of each cell in the body. They are an alternative fuel source to glucose.[note]Sato, Kiyotaka, et al. Insulin, ketone bodies (ketones), and mitochondrial energy transduction. The FASEB Journal 9.8 (1995): 651-658.[/note]
Ketones are simple compounds because of their small molecular structure and weight. Specifically, they are organic (carbon-based) compounds. They contain a central carbon atom, an oxygen atom and two carbon-containing substituents. This is “R” (see chemical structure below) [note] Stryer, Lubert. “Biochemistry, 1995.” H Freeman & Co.,, New York (1995) pp. 510–515, 581–613, 775–778. ISBN 0 7167 2009 4.[/note] [note]Zupec-Kania, Beth A., and Emily Spellman. “An Overview of the Ketogenic Diet for Pediatric Epilepsy.” Nutrition in Clinical Practice, vol. 23, no. 6, 2008, pp. 589–96, doi:10.1177/0884533608326138.[/note].
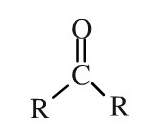
What do Ketones Look Like in Humans?
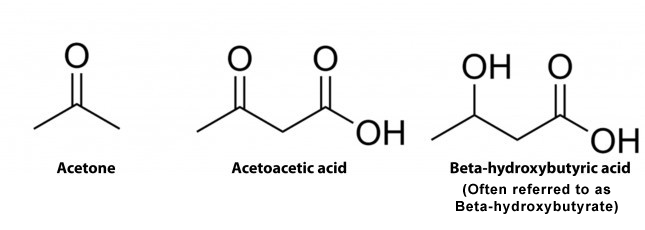
Humans make three types of ketone. These are often referred to as ‘ketone bodies’ or ‘ketones’ 2.
The three ketones are:
- Acetone
- Acetoaceate ( also know as Acetoacetic Acid)
- Beta-Hydroxybutyric Acid (also known as Beta Hydroxybuyrate or BHB). Other chemical names include 3-hydroxybutyric acid or 3-hydroxybutyrate.
It is important to note that BHB is not a ketone. This is because it contains a reactive OH-group in place of where the bound oxygen should be. You can see this in the diagram below. However, BHB still acts like a ketone in the body and converts into energy.This is similar to the other ketones acetoacetate and acetone.
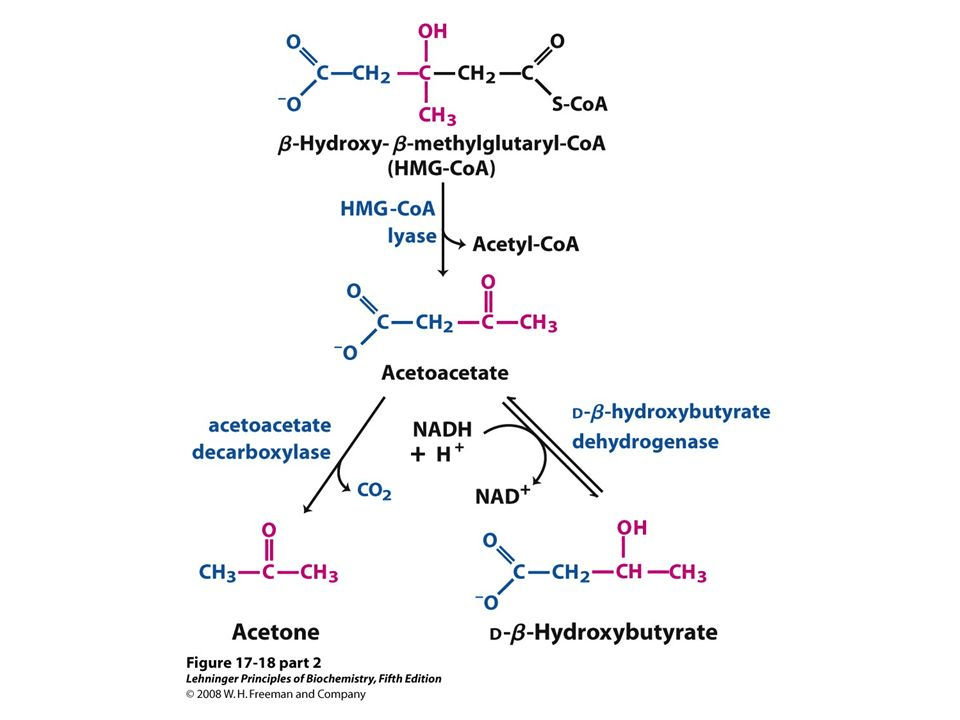
What is Ketogenesis?
Ketogenesis is the break down and use of fatty acids by β-oxidation. [note]Veech, Richard L., et al. Ketone bodies, potential therapeutic uses. IUBMB life 51.4 (2001): 241-247.[/note] This process gives acetyl CoA which then leads to β-hydroxy-β-methyglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) as seen below[note]Nelson, David L., Albert L. Lehninger, and Michael M. Cox. Lehninger principles of biochemistry. Macmillan, 2008.[/note]. HMG-CoA converts into Acetoacetone which can switch back and forth to BHB. Acetoacetone to Acetone conversion cannot be reversed (on the left below). Acetoacetate and BHB (via acetoacetate) are used to make energy. They are converted back into acetyl-CoA within a cell’s mitochondria. Meanwhile Acetone is excreted in the breath and urine.4
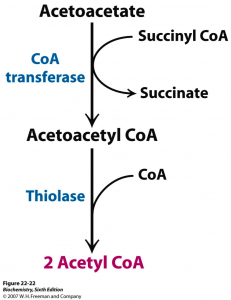
Exogenous Ketone Bodies Explained
Exogenous ketones are ketones that are ingested through a nutritional supplement. Current examples of these are Ketone Salts and Ketone Esters. Ketones made in the liver are more properly referred to as endogenous ketones.
Endogenous = Originates from inside the body.
Most supplements rely on BHB as the source of their exogenous ketones. BHB is converted to acetoacetic acid with a small amount converted to acetone through the ‘a acetoacetate decarboxylase’ waste pathway. Some of the acetoacetic acid will enter the energy pathway using beta-ketothialase. This converts acetoacetic acid into two Acetyl-CoA molecules (see diagram below2).
The Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle and generates ATP. Exogenous ketone body supplements provide users with an instant supply of ketones. They do this even if you’re not in a state of ketosis before ingestion, such as when eating a high-carb diet. They raise blood ketones even in the presence of insulin (which inhibits ketogenesis).[note]Stubbs, Brianna J., et al. (2017) On the Metabolism of Exogenous Ketones in Humans. Frontiers in Physiology, vol. 8, no. OCT, 2017, pp. 1–13, doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00848[/note]
Where is the Research?
Research is in the early stages. We need more data to understand the long-term effects of combining high blood ketone levels with high or moderate carbohydrate based diets.
We don’t yet fully understand what the long term effects of combining a non keto diet with exogenous ketone supplements are. Research is in its early stages and more data is needed.
A common question is why BHB is the go-to ketone body for exogenous ketone supplements. The likely reason is a combination of its efficient conversion into energy and its ease of formulation. In other words, it is easier to formulate BHB into a nutritional supplement. The body efficiently converts BHB to acetoacetic acid, which effectively raises blood ketone levels.
Are “Raspberry Ketones” the Same as “Ketone Bodies”?
Raspberry ketones have become an increasingly popular ingredient used in fat-loss supplements. But, despite their name, they have no relation to ketones. This has created some confusion for people interested in exogenous ketone supplements and the keto diet.
Raspberry ketones are in fact phenolic compounds that give raspberries their pleasant smell. They are structurally similar to the stimulant synephrine. Despite the marketing, raspberry ketones don’t have much effect on fat loss.[note]I.F. Gaunt, M. Sharratt, J. Colley*, A.B.G. Lansdown, P. Grasso (1970). Acute and short-term toxicity of p-hydroxybenzyl acetone in rats. Food and Cosmetics Toxicology, 8(4), 349-358.[/note]
Takeaway: Ignore information and products related to raspberry ketones. These have nothing to do with the keto diet, exogenous ketones or beta-hydroxybutyrate.
Ketone Salts vs. Ketone Esters
Exogenous ketones of beta-hydroxybutyrate are available in two forms:
- Ketone Salts: Naturally-derived compounds that simply mix sodium (and/or potassium, or calcium) with BHB to improve absorption. Commercially available supplements are all made from ketone salts currently (includes KetoForce, KetoCaNa and Keto OS). These are also sometimes called “Ketone Mineral Salts” of “BHB Mineral Salts”.
- Ketone Esters: Synthetically-made compounds that link an alcohol to a ketone body, which is metabolised in the liver to a ketone. Ketone esters are used primarily in research for testing their efficacy in elevating ketone body levels (below is a generic structure of a BHB ester). The first commercial Ketone Ester drink is now commercially available by HVMN. Research esters are very unpleasant tasting which HVMN hopes to change.
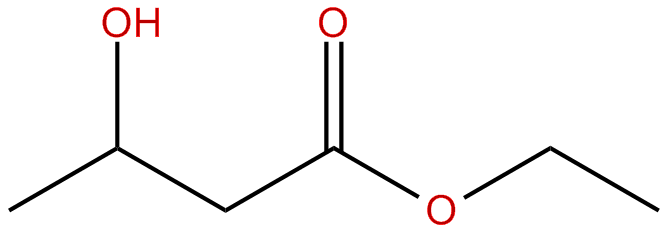
The Ketone Esters raise blood levels of beta-hydroxybutyrate to higher levels than the Ketone salts. There is also strong evidence that ketone esters are more effective than ketone salts as far as their physiological benefits go. It is not clear why this happens, but could be because of a difference in the absorption rate in the GI tract.
However, esters tend to be a little tougher to tolerate (due to gut distress after ingestion) and don’t have the most pleasant taste.
Figure 1 6 below shows a comparison ingesting equal amounts of BHB in the form of a Ketone ester and Ketone salts on blood BHB.
The supplements included:
- BMS (Beta-hydroxybutyrate Mineral Salt) – sodium/ potassium based (KetoForce)
- KE (Ketone Ester) – (R- 3-hydroxybutyl-R-1,3-hydroxybutyrate) (HVMN)
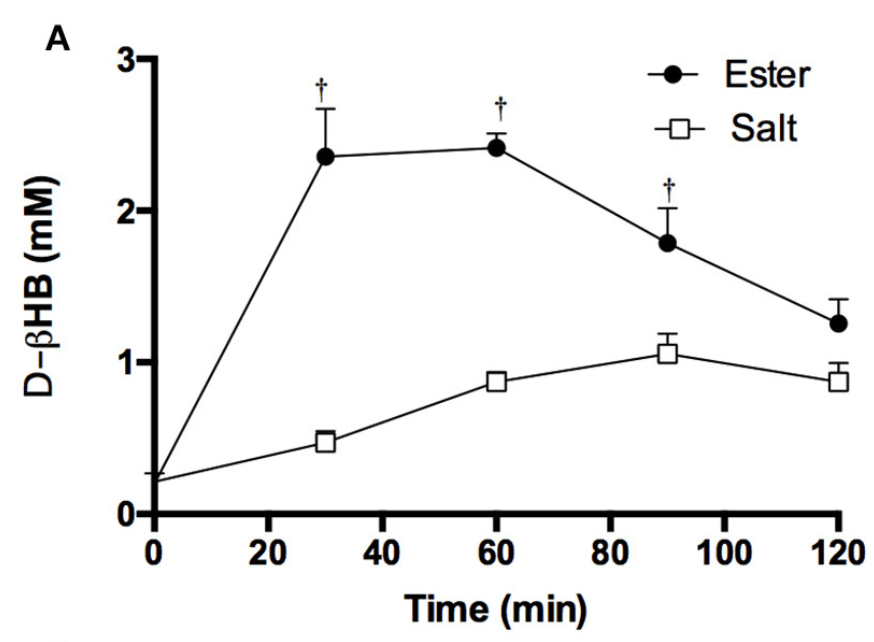
Figure 1: Blood BHB level after consuming a Ketone Ester vs Ketone Salt drink6
Why use Exogenous Ketones?
Exogenous ketone supplements may provide many benefits.
These include athletic performance enhancement, `greater weight loss, cancer prevention, cognitive improvement and anti-inflammatory properties.
Weight Loss Goals
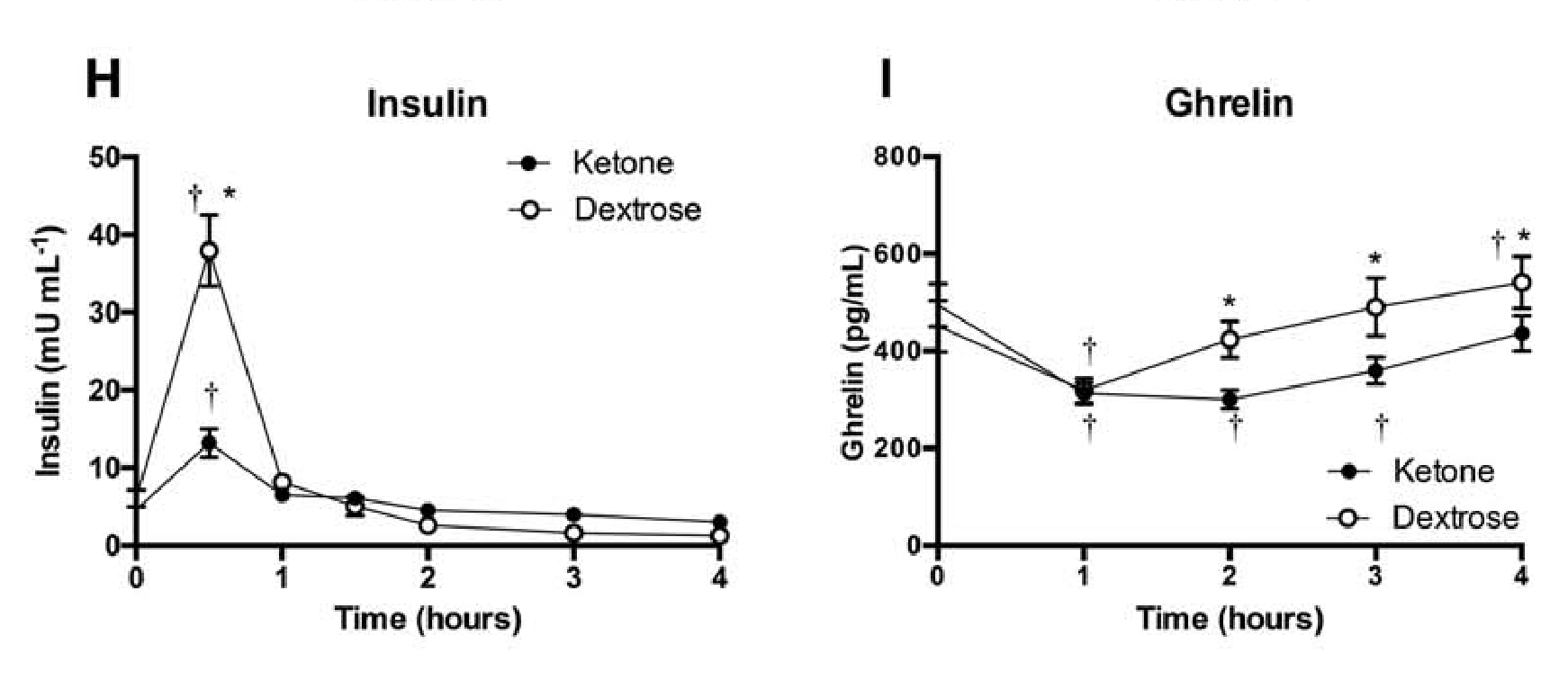
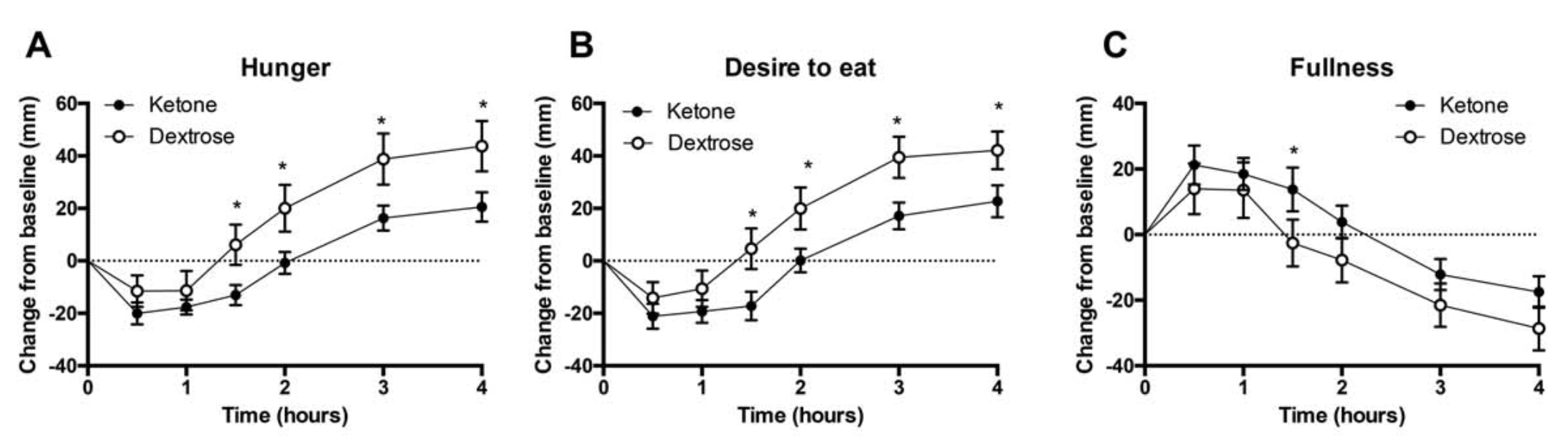
- Appetite suppression: Appetite was measured in 10 males and 5 females after consuming a ketone ester (KE) or a dextrose (DEXT) drink (sugary drink). Desire to eat and perception of hunger dropped after both drinks. However, the KE was 50% more effective for 1.5-4hrs. Insulin levels rose for both drinks but were 3x less with the KE drink after 30mins (Fig 2). The hunger hormone, ghrelin, was significantly lower between 2 to 4 hours after drinking the KE (Fig 2). In conclusion Ketone esters delay the onset of hunger and lower the desire to eat. [note]Stubbs, Brianna J., et al. A ketone ester drink lowers human ghrelin and appetite. Obesity (2017).[/note]
- The fate of excess ketones: In the event someone has an excessive amount of ketones in the blood, the body (specifically the kidneys) will work as quickly as possible to filter out ketones via urine rather than converting them to fatty adipose tissue.[note]Clark, V. L., & Kruse, J. A. (1990). Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations. JAMA, 264(21), 2808-2809.[/note] This is not to say that you can’t gain fat if you consume a large number of exogenous ketones. However, they are less likely to be converted to fat than other nutrients.
- More tolerable than MCT oil: MCT oil has been known to cause gastrointestinal distress in users, especially when taken in large amounts. However, Exogenous ketones in the form of ketone salts are well-tolerated. Thus they enable one to avoid adverse GI events while providing the body with similar types of benefits. Figure 2 shows Ketone esters can be effective at reducing appetite. A combination of MCT oil and exogenous ketones may aid weight loss and allow a lower loading of ketone supplements, without the GI distress seen with MCT oil.
Performance Goals
- Athletic enhancement: The improvement of energy efficiency and fuel sparing mechanisms. Exogenous ketone supplementation could enhance both of these components of athletic performance. There is a promising outlook in this area for a variety of reasons:
- Exogenous ketones induce acute ketosis. The effects last for several hours. This is without needing to have depleted muscle glycogen stores. (Low muscle glycogen is well known to impair sustained physical performance).[note]Cox, P. J., & Clarke, K. (2014). Acute nutritional ketosis: implications for exercise performance and metabolism” Extreme Physiology & Medicine, 3, 17. http://doi.org/10.1186/2046-7648-3-17.[/note].
- The ‘carb-sparing’ effect from BHB suppresses the break down of muscle glycogen. This leads to lower lactate levels. When increasing exercise intensity, fat oxidation (burning) reaches a limit. At that point the muscle burns carbs as fuel. But when consuming Ketone esters, the body does not make this switch. This suggests Ketones are being used instead. [note] Cox, Pete J., et al. (2016) Nutritional Ketosis Alters Fuel Preference and Thereby Endurance Performance in Athletes. Cell Metabolism, vol. 24, no. 2, Elsevier Inc., pp. 256–68, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.07.010.[/note]
- Exogenous ketones cause the body to rely less on fat as fuel (see Fig 3). Fat takes longer to metabolise for energy than muscle glycogen. This is why fatty acids are not the preferred fuel under heavy exercise. This could be useful for keto-adapted athletes performing high-intensity cardiovascular or strength training.[note] Burke, Louise M., et al. (2017)Low Carbohydrate, High Fat Diet Impairs Exercise Economy and Negates the Performance Benefit from Intensified Training in Elite Race Walkers. Journal of Physiology, vol. 595, no. 9, pp. 2785–807, doi:10.1113/JP273230.[/note] This is particularly useful for the Keto-adapted athlete who wants to undergo high-intensity cardiovascular or strength training.
- Ketone esters increase free carnitine whilst exercising. This seems to improve physical performance. [note] Wall, Benjamin T., et al. (2011) Chronic oral ingestion of l‐carnitine and carbohydrate increases muscle carnitine content and alters muscle fuel break down and usage during exercise in humans. The Journal of physiology 589.4 (2011): 963-973.[/note]
- Exogenous ketones reduce the use of Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) as fuel (deamination). Consumption of a ketone ester drink reduced the rise in muscle BCAAs by 50% during exercise. 6
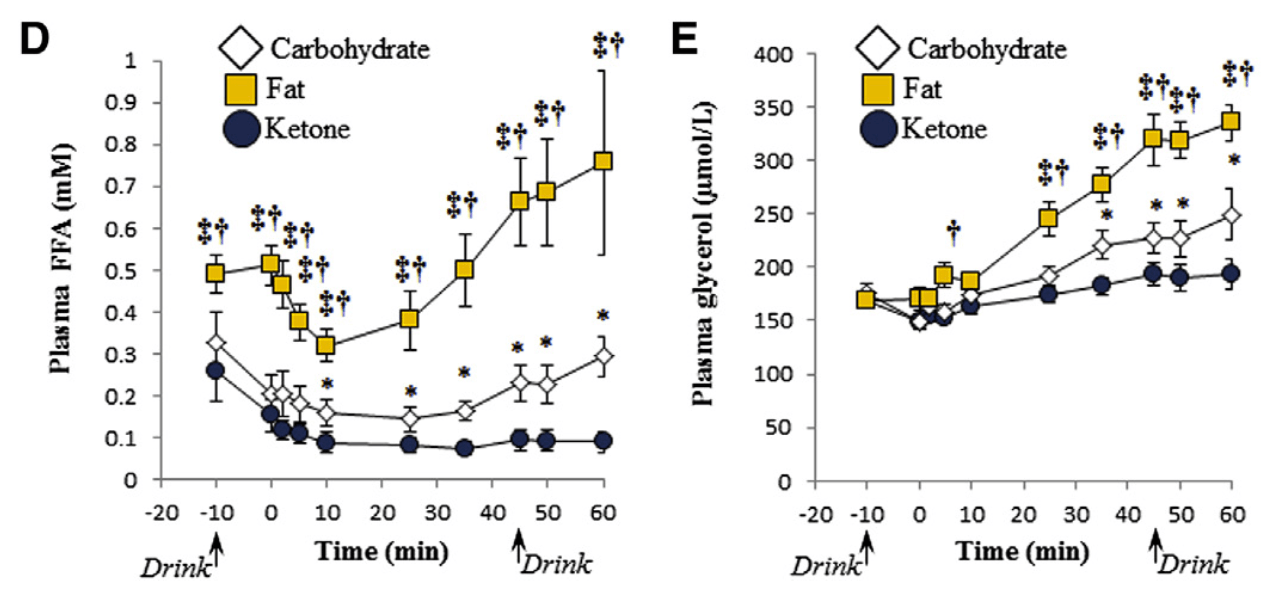
Figure 3: Plasma Free Fatty Acid (FFA) and glycerol concentrations after consuming high fat, carbohydrate or ketone ester drink6
- Improved cognition: Elevated plasma ketone concentrations divert the brain to use ketones for synthesis of phospholipids. This drives growth and myelination. Normally, glucose would be the preferred substrate, which is much less efficient.[note]Yeh, Y. Y., & Sheehan, P. M. (1985, April). Preferential usage of ketones in the brain and lung of newborn rats. In Federation proceedings (Vol. 44, No. 7, pp. 2352-2358).[/note] BHB seems to act as a signal for neuronal pathways. These enhance synaptic plasticity, cognition and neuronal stress resistance. [note]Hood, David A., et al. (2016) Unravelling the mechanisms regulating muscle mitochondrial biogenesis. Biochemical Journal 473.15 : 2295-2314.[/note] In rat studies, ingestion of a ketone ester for 5 days improved their spatial learning and memory. [note]Murray, Andrew J., et al. (2016) Novel ketone diet enhances physical and cognitive performance. The FASEB Journal 30.12: 4021-4032.[/note].
Health & Longevity
- Anti-carcinogenic properties: Data suggests that exogenous ketones are an effective anti-carcinogen. The reason behind this is that cancer cells are unable to use ketones effectively, unlike most healthy tissues in the body. In fact, dietary ketone supplementation has been shown to increase survival rates of mice with systematic cancer by as much as 70%.[note]Poff, A. M., Ari, C., Arnold, P., Seyfried, T. N., & D’Agostino, D. P. (2014). Ketone supplementation decreases tumor cell viability and prolongs survival of mice with metastatic cancer. International journal of cancer, 135(7), 1711-1720.[/note]
- Neuroprotection: As humans age, the brain becomes more susceptible to neurodegeneration and subsequent conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Exogenous ketone supplementation appears to ameliorate the typical decline in cognitive function that comes with aging. The likely mechanism here is that ketones reduce the inflammation and hyperexcitability that is normally exhibited as glucose break down and usage declines in the brain.[note]Hashim, S. A., & VanItallie, T. B. (2014). Ketone body therapy: from the keto diet to the oral administration of ketone ester. Journal of lipid research, 55(9), 1818-1826.[/note], [note]Hertz, L., Chen, Y., & Waagepetersen, H. S. (2015). Effects of ketone bodies in Alzheimer’s disease in relation to neural hypometabolism, β‐amyloid toxicity, and astrocyte function. Journal of neurochemistry, 134(1), 7-20.[/note]
- Anti-Inflammatory properties: There is evidence that ketones play a crucial role in reducing inflammation. They inhibit a specific class of proteins called inflammasones.[note]Youm, Y. H., Nguyen, K. Y., Grant, R. W., Goldberg, E. L., Bodogai, M., Kim, D., … & Kang, S. (2015). The ketone metabolite [beta]-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nature medicine, 21(3), 263-269.[/note]
- Gene regulation profile change. There is evidence that gene sets can be up regulated or down regulated. An example of this is a change in mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase (mHS) in rats on a keto diet. The research is still in its early days.
How Exogenous Ketones Work
Exogenous ketones have a variety of physiological effects shortly after consuming:
- For starters, ingesting ketones (especially ketone esters) is an efficient way to elevate BHB in the blood by upwards of 2 mMol. Levels can stay elevated for nearly 8 hours (see Ref. 2). Ketone salts don’t appear to elevate BHB in the blood as efficiently or significantly as ketone esters.
- Exogenous ketone supplementation causes blood glucose to decrease significantly. This is likely due to the acute increase in insulin sensitivity. Therefore, exogenous ketones may present a potential therapy for type-2 diabetics through blood glucose regulation.
- Exogenous ketones also improve oxygen utilization. This is seen especially in the central nervous system (CNS).[note] D’Agostino, D. P., Pilla, R., Held, H. E., Landon, C. S., Puchowicz, M., Brunengraber, H., … & Dean, J. B. (2013). Therapeutic ketosis with ketone ester delays central nervous system oxygen toxicity seizures in rats. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 304(10), R829-R836.[/note] This effect decreases the likelihood of oxygen reaching toxic levels in the CNS. This in turn has a number of other positive health ramifications, such as those discussed in the previous section.
Possible Downsides to Ketone Supplementation
As with almost any nutritional supplement, side effects and downsides are possible after consuming exogenous ketones. That being said, they tend to be benign and will most likely improve as exogenous ketone supplementation becomes more prominent. The most common side effects to be aware of when using exogenous ketones include:
-
Electrolyte Imbalance
The reasoning behind electrolytes becoming depleted during a state of ketosis is due to lack of water retention and frequent urination. When supplementing with exogenous ketones, the acute state of ketosis will likely increase the frequency of urination. However, it won’t deplete glycogen stores. Therefore, it may be useful to drink an electrolyte solution if you are urinating a lot after taking exogenous ketones. However, it is dependent upon how you feel.
-
Halitosis (bad breath)
If you’re on a keto diet you are probably aware that as the body starts to metabolize fat, ketones can cause poor breath. Unfortunately, there is very little one can do about this, it is just the nature of the beast. Thus, this can also arise when using exogenous ketones. Thankfully, it is not as long lasting as when on a keto diet. Chewing gum or mints is the best option if it becomes a noticeable issue. Ultimately, this may be caused by over consumption of the ketone supplement. Therefore, tailoring the quantity consumed may prevent excess BHB being converted to acetone, which is likely excreted by the lungs.
-
Possible GI distress (flatulence) at exceptionally high doses
In the studies referenced in this article, exogenous ketones taken in large doses occasionally resulted in GI distress, especially flatulence. However, the cause of this is hypothesized to be due to the fact that ketones were mixed in a milky fluid that wasn’t very palatable. If you’re taking a nominal dose of exogenous ketones the likelihood of GI distress is rather low. Moreover, if some GI distress is prevalent, it should improve as you become accustomed to taking ketones.
-
Hypoglycemia: Why Not To Be Concerned
Taking exogenous ketones can drive blood glucose levels quite low. However, you are not likely to feel the typical symptoms of hypoglycemia. This is because when ketone levels are high enough, they dominate as fuel in the brain. Therefore, you will feel just fine despite having low blood glucose. A highly-cited study by George Cahill, found elevated ketone levels could protect fasted participants when they were administered insulin to induce hypoglycemia.
Future Applications & Research
Most current research on exogenous ketones focuses on the health and longevity applications of their use. Much of Dominic D’Agostino’s current work is on the cancer prevention aspect of exogenous ketones.
Another area that is targeted, is the psychological benefits of exogenous ketones, especially with how they can help protect brain tissue from degradation. As mentioned earlier, this has implications for the prevention of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epileptic seizures.
Hopefully, future research will focus more on the athletic performance benefits of exogenous ketones, specifically with regards to resistance training and cardiovascular exercise. The data on each of these applications is very limited at this time.
Further Reading & Recommended Resources
There are a limited group of individuals we recommend you follow to keep up with current findings on exogenous ketones. See the links below:
-
Dominic D’Agostino, Ph.D
Dominic D’Agostino has done research focusing on cancer prevention with exogenous ketones. Dominic’s research and his lab at the University of Southern Florida has led the way in the area of exogenous ketones in the U.S. We interviewed Dominic here.
-
Peter Attia, M.D.
Peter Attia is a surgeon who studied at Stanford Medical School and did his residency at Johns Hopkins University. He has a passion for helping others lose weight, increase their longevity, and improve their performance (physically and mentally). He has experimented heavily with ketosis, exogenous ketones and keto diets.
-
Dr. Richard Veech
Richard Veech is the senior investigator at the Laboratory of Metabolic Control in Rockville, MD, USA. His research focuses heavily on the role of ketones in regards to preventing metabolic diseases, such as type-2 diabetes.
-
Patrick Arnold
Patrick Arnold is an organic chemist who is notorious for being the creator of several performance-enhancing steroids. He is arguably one of the strongest influencers on the advancement of sports supplementation. Currently he is focused on developing products under the KetoSports brand, which includes two exogenous ketone products – KetoForce and KetoCaNa.
-
Kieran Clarke
Kieran Clarke is a researcher at Oxford University in the UK. She has authored research around their use in athletic performance.
Quality Interviews and Blog Posts
- STEM-Talk Interview discussing “Ketone esters and their application in sport” featuring Dr. Brianna Stubbs
- The Eating Academy: Blog post from Dr. Peter Attia on “My Experience with Exogenous Ketones”
- Quantified Body Podcast: 2 hour long interview discussing the safety, effectiveness and status of ketone mineral salts featuring Dr. Dominic D’Agostino.
- Dominic D’Agostino has two in-depth interviews on The Tim Ferriss Show (Part 1, Part 2). Discussion includes exogenous ketones for mitigating the onset of neurodegenerative diseases, using ketones in place of fasting for chemo-protection, benefits of ketone supplementation when consuming carbohydrates, the risks and potential toxicities of ketones.
- KetoVangelist: Dr. Dominic D’Agostino discusses his work with exogenous ketones
Summary Takeaways
Exogenous ketones are becoming a popular topic of research. Importantly, research aims to validate their various uses (physical performance, weight loss, neuroprotective effects etc.). While there is good research on many of these, more data is needed to provide conclusive evidence.
Exogenous ketones, especially Ketone Esters, achieve ketosis without following a keto diet. However, they must be consumed regularly to maintain ketosis. If Ketones are readily available, they will be used preferential over carbohydrates and fats when exercising. Even in highly glycolytic (carbohydrate) activities, such as sprinting. (Learn more about Ketone Esters in this complete Ketone Ester research review)
Exogenous ketones certainly appear to have strong health and longevity properties at this point. Interesting areas such as reducing the risk of cancer and possibly preventing/remitting type-2 diabetes. We recommend reading more from the resources listed above as they are the foremost authorities on research in exogenous ketones.
Next read Part II in our exogenous ketone series, on exogenous ketone supplements to understand the current ketone supplements available.