ONE Actionable Takeaway from Ketosource
One of the top complaints we get about fasting is trouble with sleep. This is largely due to the promotion of sleep-disturbing hormones.
The most effective way to solve this is a four-step process.
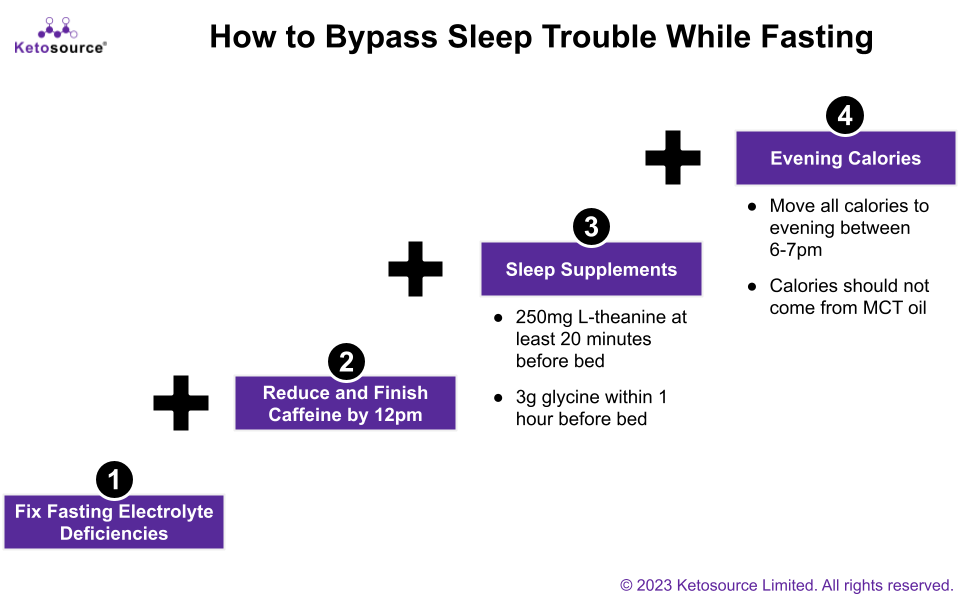
Start with just the first step. You only need to take extra steps, one by one, should the problem persist. Most people won’t need to do all four.
- Electrolytes: Use our electrolyte calculator to solve deficiencies.
- Caffeine: Finish all caffeine intake by 12pm and reduce your daily intake if you still feel alert by bedtime.
- Sleep Supplements: Take l-theanine and glycine before bedtime as they help with sleep.
- Evening calories: Move all or some of the calories you eat on your fasting days to the evening between 6 and 7 pm (e.g. your one meal of the day). But don’t take MCT oil in the evening as it can promote sleep issues for some people.
Research References
- The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine (reviewed in ) are involved in waking/ wakefulness
- Reducing blood sugar is associated with the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine
- Reduced sodium intake is associated with increased epinephrine and norepinephrine
- Magnesium deficiency is associated with increased epinephrine and norepinephrine in rats
- Caffeine promotes wakefulness (reviewed in )
- Theanine improves sleep quality at doses as low as 250mg
- Theanine may take effect as soon as 15 minutes after taking it, though it can take longer to reach peak plasma levels
- Taking 3g of glycine within one hour before bed can improve various aspects of sleep quality
- We do not have evidence from the literature relating sleep to eating calories before bed. But foods may promote sleep via mechanisms tied to blood sugar and electrolytes as outlined here. So we suspect that eating some calories before sleep may promote sleep as well.
- Anecdotal evidence from clients suggests that MCT oils may disrupt sleep when taken too close to bedtime. Though we don’t know the exact mechanism for this, we suspect that it involves the metabolism of MCT oils. Based on the ketogenic response to MCT oils (plus buffer time), we recommend keeping at least 4 hours between your last dose of MCT and bedtime.
ONE Quote from a Credible Expert
How the ketogenic diet impacted military personnel from Dr. Jeff Volek. Jeff is a professor researching ketogenic diets in the Department of Human Sciences at Ohio State University. He’s also a founder of Virta Health, the company successfully reversing type 2 diabetes via ketogenic diets:
“The results [of our study on military personnel] were quite extraordinary… the protocol, that we use in, in studies, we don’t prescribe calories in a lot of these free living studies. So, we really enforce the low-carb piece of it and monitor ketones, but we allow people to eat, as, until, they’re full.
So, “eat to satiety” is what we say. So, there was no recommendation to restrict calories.
Yet, every single participant lost weight. And we measured body composition by, you know, arguably the gold standard, DEXA, and they were, able to demonstrate remarkable improvement in body composition as well. So, they’re actually, you know, maintaining most of their lean mass while losing a lot of fat mass.”
Source: Ketogenic Diet to improve metabolic health and treat disease | STEM Talk Episode 149 | 23 February 2023 (timestamp:
00:43:35)
Research References
- The research study that Dr. Volek is referencing
ONE of Your #1 Questions Answered
The Question:
The top question sent in from you this week was from Rami Khateeb. Thank you Rami!
“What are your thoughts on Exogenous Ketones supplements if someone is taking them without following a ketogenic diet? And what is your opinion of different brands like the one from Pruvit company (keto//os)?”
The Answer:
Exogenous Ketones without a Ketogenic Diet
Exogenous ketone supplements will increase your ketone level regardless of your diet. Research I’ve read supports this as well as internal experiments we ran at Ketosource.
So if you prefer not to follow a ketogenic diet, you can still expect a ketone boost from exogenous ketones.
Evaluating Specific Exogenous Ketone Supplements
There are four types of exogenous ketone supplements: ketone salts, ketone esters, MCT oils and 1,3 Butanediol.
We have run experiments to test the peak ketone boost per serving of several of these supplements. We then also benchmarked the cost per serving for each supplement. The chart below illustrates this analysis.
As you can see, there is a wide range of prices per serving and peak ketone boost for exogenous ketone supplements.

The Takeaway
- Aim for your minimum effective ketone boost. More is not necessarily better. The ketone boost you should aim for depends on your goal. For fat loss, appetite reduction ketosis is all you need (0.5 mmol/L). For other goals, it can be higher.
- Get the most value by comparing exogenous ketone supplements on a cost per serving basis. Compare exogenous ketone supplements that meet your ketone boost needs on a cost per serving basis. That way you can meet your goal at the lowest cost.
Research References
- Exogenous ketone experiment data: Ketosource analysis, Ketosource N=2 experiment data sets. Public recommended retail price (RRP) used.
- Note that the specific supplement formulations and their behavior may have changed since this experiment. Yet, the general comparison between ketone esters vs. ketone salts vs. C8 MCT will hold true. Read the full details on the experiment here.
- Ketone salts, ketone esters, MCT oils, and 1,3-butanediol can all boost ketone levels.
Want your question answered in next week’s
KET-ONE Sunday?
Just hit reply to this email and ask your question.
Continuous Ketone Monitor Experiment – What You Decided to Test
I’m guinea-pigging myself in a continuous ketone monitor self-experiment.
I crowd sourced what the experiment should be last week with you. And here’s what you voted on.

Next steps? We will design the 14-day experiment to include your four top-voted experiments (the black segments from the chart above).
Then it will be guinea-pig time. A big thanks to everyone who voted on ‘one night of poor sleep’ by the way – the things I do for citizen science!
I’ll update you in future editions of KET-ONE Sunday as this unfolds.
Research References
{5748374:AGHXG472},{5748374:RUSEBBWR},{5748374:VL3JPWJF};{5748374:RYIRW9EH};{5748374:GMWZVET5};{5748374:4L8IQSVH};{5748374:7AYQNPZJ};{5748374:RYIRW9EH};{5748374:8MPB5CG6},{5748374:87QDTP7J};{5748374:6R5D2T76};{5748374:GSG39E7Z};{5748374:VXTTQ9XK};{5748374:VKS54E7J};{5748374:IQVIATN4};{5748374:P9KSH38T};{5748374:P9KSH38T};{5748374:VKS54E7J};{5748374:YANL5G5Z}
3d-printed-materials-and-systems
default
asc
0
10322
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A950%2C%22request_next%22%3A50%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%22PNNNMDCY%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Dietze%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%221976%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BDietze%20G%2C%20Wicklmayr%20M%2C%20Grunst%20J%2C%20Mehnert%20H%20%281976%29%20%5BThe%20anti-ketogenic%20effect%20of%20fructose%5D.%20Verh%20Dtsch%20Ges%20Inn%20Med%2082%20Pt%201%3A767%26%23x2013%3B769%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22%5BThe%20anti-ketogenic%20effect%20of%20fructose%5D%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dietze%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wicklmayr%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Grunst%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mehnert%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%221976%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22ger%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220070-4067%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-04-17T10%3A10%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UMT4FS8S%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lee%20and%20Wolever%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%221998-12%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLee%20BM%2C%20Wolever%20TM%20%281998%29%20Effect%20of%20glucose%2C%20sucrose%20and%20fructose%20on%20plasma%20glucose%20and%20insulin%20responses%20in%20normal%20humans%3A%20comparison%20with%20white%20bread.%20Eur%20J%20Clin%20Nutr%2052%3A924%26%23x2013%3B928.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Fsj.ejcn.1600666%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Fsj.ejcn.1600666%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effect%20of%20glucose%2C%20sucrose%20and%20fructose%20on%20plasma%20glucose%20and%20insulin%20responses%20in%20normal%20humans%3A%20comparison%20with%20white%20bread%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lee%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wolever%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22OBJECTIVE%3A%20To%20determine%20the%20plasma%20glucose%20and%20insulin%20responses%20of%20various%20doses%20of%20glucose%2C%20sucrose%2C%20fructose%20and%20white%20bread%20in%20normal%20human%20subjects.%5CnDESIGN%3A%20Plasma%20glucose%20and%20insulin%20were%20measured%20before%20and%20at%20various%20times%20after%208%20subjects%20ate%2013%20different%20test%20meals%20in%20randomized%20order%20on%20separate%20days%20after%20an%20overnight%20fast.%20Test%20meals%20consisted%20of%20500%20ml%20of%20tea%20or%20water%20to%20which%20was%20added%20either%20nothing%2C%2025%2C%2050%2C%20or%20100%20g%20of%20glucose%20or%20sucrose%2C%2025%20or%2050%20g%20fructose%2C%2050%20g%20glucose%20plus%2050%20g%20fructose%2C%20or%20a%2025%2C%2050%20or%20100%20g%20carbohydrate%20portion%20of%20white%20bread.%20The%20glycaemic%20%28GI%29%20and%20insulinaemic%20index%20%28II%29%20values%20of%20the%20sugars%20were%20calculated%20by%20expressing%20the%20incremental%20areas%20under%20the%20plasma%20glucose%20and%20insulin%20curves%20%28AUC%29%20after%20glucose%2C%20sucrose%20and%20fructose%20as%20a%20percentage%20of%20the%20respective%20AUC%20after%20white%20bread%20containing%20the%20same%20amount%20of%20carbohydrate.%5CnSETTING%3A%20University%20teaching%20hospital%20clinical%20nutrition%20centre.%5CnSUBJECTS%3A%20Lean%2C%20normal%20subjects%20%284%20male%2C%204%20female%29%2021-33%20y%20of%20age.%5CnRESULTS%3A%20Plasma%20insulin%20responses%20increased%20nearly%20linearly%20as%20carbohydrate%20intake%20increased%20from%200%20to%20100%20g%2C%20but%20glycaemic%20responses%20increased%20by%20only%2068%25%20and%2038%25%20as%20carbohydrate%20intake%20increased%20from%2025%20to%2050%20g%20and%2050%20to%20100g%2C%20respectively.%20The%20GI%20and%20II%20values%20of%20glucose%2C%20149%2B%5C%2F-16%20and%20147%2B%5C%2F-18%2C%20respectively%2C%20were%20significantly%20greater%20than%20those%20of%20bread%20%28100%3B%20P%26lt%3B0.05%29%2C%20while%20the%20values%20for%20fructose%2C%2016%2B%5C%2F-4%20and%2022%2B%5C%2F-3%20were%20significantly%20less%20than%20those%20of%20bread%20%28P%26lt%3B0.001%29.%20GI%20values%20did%20not%20differ%20significantly%20from%20II%20values.%5CnCONCLUSIONS%3A%20It%20is%20concluded%20that%2C%20in%20normal%20subjects%2C%20as%20carbohydrate%20intake%20is%20increased%20from%200%20to%20100%20g%2C%20plasma%20insulin%20responses%20increase%20at%20a%20greater%20rate%20than%20plasma%20glucose%20responses.%20The%20insulinaemic%20responses%20elicited%20by%20glucose%2C%20sucrose%20or%20fructose%20are%20similar%20to%20those%20that%20would%20be%20expected%20from%20a%20starchy%20food%20with%20the%20same%20glycaemic%20index.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22Dec%201998%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22eng%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1038%5C%2Fsj.ejcn.1600666%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220954-3007%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%226ZD5MYAL%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-04-17T10%3A08%3A36Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%226X22CVSE%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BHypometabolism%20as%20a%20therapeutic%20target%20in%20Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20disease%20%7C%20SpringerLink.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1471-2202-9-S2-S16%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1471-2202-9-S2-S16%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2030%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Hypometabolism%20as%20a%20therapeutic%20target%20in%20Alzheimer%27s%20disease%20%7C%20SpringerLink%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1471-2202-9-S2-S16%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T11%3A48%3A44Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22VCPKRBSX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BDietary%20ketosis%20enhances%20memory%20in%20mild%20cognitive%20impairment%20-%20ScienceDirect.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fabs%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0197458010004392%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fabs%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0197458010004392%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2030%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Dietary%20ketosis%20enhances%20memory%20in%20mild%20cognitive%20impairment%20-%20ScienceDirect%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fabs%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0197458010004392%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T11%3A46%3A44Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BDH7M7EZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAlzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease%20is%20Type%203%20Diabetes%26%23x2014%3BEvidence%20Reviewed%20-%20Suzanne%20M.%20de%20la%20Monte%2C%20Jack%20R.%20Wands%2C%202008.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1177%5C%2F193229680800200619%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1177%5C%2F193229680800200619%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2030%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Alzheimer%27s%20Disease%20is%20Type%203%20Diabetes%5Cu2014Evidence%20Reviewed%20-%20Suzanne%20M.%20de%20la%20Monte%2C%20Jack%20R.%20Wands%2C%202008%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1177%5C%2F193229680800200619%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T11%3A42%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22RWXZB9WD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BFeasibility%20and%20efficacy%20data%20from%20a%20ketogenic%20diet%20intervention%20in%20Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20disease%20-%20ScienceDirect.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS2352873717300707%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS2352873717300707%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2030%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Feasibility%20and%20efficacy%20data%20from%20a%20ketogenic%20diet%20intervention%20in%20Alzheimer%27s%20disease%20-%20ScienceDirect%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS2352873717300707%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T11%3A27%3A13Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22E7CGIUQT%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Pawlosky%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222020-02-04%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPawlosky%20RJ%2C%20Kashiwaya%20Y%2C%20King%20MT%2C%20Veech%20RL%20%282020%29%20A%20Dietary%20Ketone%20Ester%20Normalizes%20Abnormal%20Behavior%20in%20a%20Mouse%20Model%20of%20Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease.%20IJMS%2021%3A1044.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijms21031044%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijms21031044%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20Dietary%20Ketone%20Ester%20Normalizes%20Abnormal%20Behavior%20in%20a%20Mouse%20Model%20of%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20Disease%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robert%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pawlosky%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yoshihero%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kashiwaya%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20Todd%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22King%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Veech%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Because%20of%20a%20decreased%20sensitivity%20toward%20insulin%2C%20a%20key%20regulator%20of%20pyruvate%20dehydrogenase%20%28PDH%29%2C%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20patients%20have%20lower%20brain%20glucose%20utilization%20with%20reductions%20in%20Tricarboxylic%20Acid%20%28TCA%29%20cycle%20metabolites%20such%20as%20citrate%2C%20a%20precursor%20to%20n-acetyl-aspartate.%20In%20the%203xTgAd%20mouse%20model%20of%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease%20%28AD%29%2C%20aging%20mice%20also%20demonstrate%20low%20brain%20glucose%20metabolism.%20Ketone%20metabolism%20can%20overcome%20PDH%20inhibition%20and%20restore%20TCA%20cycle%20metabolites%2C%20thereby%20enhancing%20amino%20acid%20biosynthesis.%20A%20ketone%20ester%20of%20d-%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20was%20incorporated%20into%20a%20diet%20%28Ket%29%20and%20fed%20to%203xTgAd%20mice.%20A%20control%20group%20was%20fed%20a%20calorically%20matched%20diet%20%28Cho%29.%20At%2015%20months%20of%20age%2C%20the%20exploratory%20and%20avoidance-related%20behavior%20patterns%20of%20the%20mice%20were%20evaluated.%20At%2016.5%20months%20of%20age%2C%20the%20animals%20were%20euthanized%2C%20and%20their%20hippocampi%20were%20analyzed%20for%20citrate%2C%20%5Cu03b1-ketoglutarate%2C%20and%20amino%20acids.%20In%20the%20hippocampi%20of%20the%20Ket-fed%20mice%2C%20there%20were%20higher%20concentrations%20of%20citrate%20and%20%5Cu03b1-ketoglutarate%20as%20well%20as%20higher%20concentrations%20of%20glutamate%2C%20aspartate%20and%20n-acetyl-aspartate%20compared%20with%20controls.%20There%20were%20positive%20associations%20between%20%281%29%20concentrations%20of%20aspartate%20and%20n-acetyl-aspartate%20%28n%20%3D%2014%2C%20R%20%3D%200.9327%29%2C%20and%20%282%29%20%5Cu03b1-ketoglutarate%20and%20glutamate%20%28n%20%3D%2014%2C%20R%20%3D%200.8521%29%20in%20animals%20maintained%20on%20either%20diet.%20Hippocampal%20n-acetyl-aspartate%20predicted%20the%20outcome%20of%20several%20exploratory%20and%20avoidance-related%20behaviors.%20Ketosis%20restored%20citrate%20and%20%5Cu03b1-ketoglutarate%20in%20the%20hippocampi%20of%20aging%20mice.%20Higher%20concentrations%20of%20n-acetyl-aspartate%20corresponded%20with%20greater%20exploratory%20activity%20and%20reduced%20avoidance-related%20behavior.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222020-02-04%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fijms21031044%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221422-0067%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F1422-0067%5C%2F21%5C%2F3%5C%2F1044%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T11%3A22%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22N7L4Y9YZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rafi%20and%20Alavi%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222017-08-30%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BRafi%20MA%2C%20Alavi%20A%20%282017%29%20Debate%20on%20human%20aging%20and%20lifespan.%20Bioimpacts%207%3A135%26%23x2013%3B137.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.15171%5C%2Fbi.2017.16%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.15171%5C%2Fbi.2017.16%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Debate%20on%20human%20aging%20and%20lifespan%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mohammad%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rafi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Abass%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Alavi%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222017-08-30%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.15171%5C%2Fbi.2017.16%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222228-5660%2C%202228-5652%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fbi.tbzmed.ac.ir%5C%2FAbstract%5C%2Fbi-17493%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A48%3A50Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22EX3J7PVP%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Crimmins%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BCrimmins%20EM%20%282015%29%20Lifespan%20and%20Healthspan%3A%20Past%2C%20Present%2C%20and%20Promise.%20GERONT%2055%3A901%26%23x2013%3B911.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgeront%5C%2Fgnv130%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgeront%5C%2Fgnv130%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Lifespan%20and%20Healthspan%3A%20Past%2C%20Present%2C%20and%20Promise%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eileen%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crimmins%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fgeront%5C%2Fgnv130%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220016-9013%2C%201758-5341%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Facademic.oup.com%5C%2Fgerontologist%5C%2Farticle-lookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgeront%5C%2Fgnv130%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A48%3A09Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%223JWL79XX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Huang%20and%20Mark%20Jacquez%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222017-05-28%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BHuang%20Y%2C%20Mark%20Jacquez%20G%20%282017%29%20Identification%20of%20a%20Blue%20Zone%20in%20a%20Typical%20Chinese%20Longevity%20Region.%20IJERPH%2014%3A571.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijerph14060571%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijerph14060571%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Identification%20of%20a%20Blue%20Zone%20in%20a%20Typical%20Chinese%20Longevity%20Region%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Huang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Geoffrey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mark%20Jacquez%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222017-05-28%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fijerph14060571%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221660-4601%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F1660-4601%5C%2F14%5C%2F6%5C%2F571%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A44%3A11Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BBWNJ6WM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Poulain%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222004%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPoulain%20M%2C%20Pes%20GM%2C%20Grasland%20C%2C%20et%20al%20%282004%29%20Identification%20of%20a%20geographic%20area%20characterized%20by%20extreme%20longevity%20in%20the%20Sardinia%20island%3A%20the%20AKEA%20study.%20Experimental%20Gerontology%2039%3A1423%26%23x2013%3B1429.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.exger.2004.06.016%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.exger.2004.06.016%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Identification%20of%20a%20geographic%20area%20characterized%20by%20extreme%20longevity%20in%20the%20Sardinia%20island%3A%20the%20AKEA%20study%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Poulain%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Giovanni%20Mario%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pes%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Claude%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Grasland%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ciriaco%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carru%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Luigi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ferrucci%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Giovannella%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Baggio%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Claudio%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Franceschi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Luca%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deiana%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%229%5C%2F2004%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.exger.2004.06.016%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2205315565%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0531556504002141%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A42%3A41Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BWIHNYER%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BMetabolic%20Syndrome%20and%20Risk%20of%20Cancer%20%7C%20Diabetes%20Care.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fcare.diabetesjournals.org%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F35%5C%2F11%5C%2F2402.abstract%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fcare.diabetesjournals.org%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F35%5C%2F11%5C%2F2402.abstract%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2030%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Metabolic%20Syndrome%20and%20Risk%20of%20Cancer%20%7C%20Diabetes%20Care%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fcare.diabetesjournals.org%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F35%5C%2F11%5C%2F2402.abstract%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A26%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22HIHTSGMM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Esposito%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-11-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BEsposito%20K%2C%20Chiodini%20P%2C%20Colao%20A%2C%20et%20al%20%282012%29%20Metabolic%20Syndrome%20and%20Risk%20of%20Cancer%3A%20A%20systematic%20review%20and%20meta-analysis.%20Diabetes%20Care%2035%3A2402%26%23x2013%3B2411.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.2337%5C%2Fdc12-0336%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.2337%5C%2Fdc12-0336%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Metabolic%20Syndrome%20and%20Risk%20of%20Cancer%3A%20A%20systematic%20review%20and%20meta-analysis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Esposito%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chiodini%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Colao%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lenzi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Giugliano%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22OBJECTIVEdAvailable%20evidence%20supports%20the%20emerging%20hypothesis%20that%20metabolic%20syndrome%20may%20be%20associated%20with%20the%20risk%20of%20some%20common%20cancers.%20We%20did%20a%20systematic%20review%20and%20metaanalysis%20to%20assess%20the%20association%20between%20metabolic%20syndrome%20and%20risk%20of%20cancer%20at%20different%20sites.%20RESEARCH%20DESIGN%20AND%20METHODSdWe%20conducted%20an%20electronic%20search%20for%20articles%20published%20through%20October%202011%20without%20restrictions%20and%20by%20reviewing%20reference%20lists%20from%20retrieved%20articles.%20Every%20included%20study%20was%20to%20report%20risk%20estimates%20with%2095%25%20CIs%20for%20the%20association%20between%20metabolic%20syndrome%20and%20cancer.%5CnRESULTSdWe%20analyzed%20116%20datasets%20from%2043%20articles%2C%20including%2038%2C940%20cases%20of%20cancer.%20In%20cohort%20studies%20in%20men%2C%20the%20presence%20of%20metabolic%20syndrome%20was%20associated%20with%20liver%20%28relative%20risk%201.43%2C%20P%20%2C%200.0001%29%2C%20colorectal%20%281.25%2C%20P%20%2C%200.001%29%2C%20and%20bladder%20cancer%20%281.10%2C%20P%20%3D%200.013%29.%20In%20cohort%20studies%20in%20women%2C%20the%20presence%20of%20metabolic%20syndrome%20was%20associated%20with%20endometrial%20%281.61%2C%20P%20%3D%200.001%29%2C%20pancreatic%20%281.58%2C%20P%20%2C%200.0001%29%2C%20breast%20postmenopausal%20%281.56%2C%20P%20%3D%200.017%29%2C%20rectal%20%281.52%2C%20P%20%3D%200.005%29%2C%20and%20colorectal%20%281.34%2C%20P%20%3D%200.006%29%20cancers.%20Associations%20with%20metabolic%20syndrome%20were%20stronger%20in%20women%20than%20in%20men%20for%20pancreatic%20%28P%20%3D%200.01%29%20and%20rectal%20%28P%20%3D%200.01%29%20cancers.%20Associations%20were%20different%20between%20ethnic%20groups%3A%20we%20recorded%20stronger%20associations%20in%20Asia%20populations%20for%20liver%20cancer%20%28P%20%3D%200.002%29%2C%20in%20European%20populations%20for%20colorectal%20cancer%20in%20women%20%28P%20%3D%200.004%29%2C%20and%20in%20U.S.%20populations%20%28whites%29%20for%20prostate%20cancer%20%28P%20%3D%200.001%29.%5CnCONCLUSIONSdMetabolic%20syndrome%20is%20associated%20with%20increased%20risk%20of%20common%20cancers%3B%20for%20some%20cancers%2C%20the%20risk%20differs%20betweens%20sexes%2C%20populations%2C%20and%20de%5Cufb01nitions%20of%20metabolic%20syndrome.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-11-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.2337%5C%2Fdc12-0336%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220149-5992%2C%201935-5548%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fcare.diabetesjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.2337%5C%2Fdc12-0336%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A26%3A40Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22NJAIXK92%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BObesity%20and%20Risk%20of%20Cancer%3A%20An%20Introductory%20Overview%20%7C%20SpringerLink.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2Fchapter%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2F978-3-319-42542-9_1%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2Fchapter%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2F978-3-319-42542-9_1%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2030%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Obesity%20and%20Risk%20of%20Cancer%3A%20An%20Introductory%20Overview%20%7C%20SpringerLink%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2Fchapter%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2F978-3-319-42542-9_1%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A20%3A58Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22V5LNMCKW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Seeman%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222004%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BSeeman%20TE%2C%20Crimmins%20E%2C%20Huang%20M-H%2C%20et%20al%20%282004%29%20Cumulative%20biological%20risk%20and%20socio-economic%20differences%20in%20mortality%3A%20MacArthur%20Studies%20of%20Successful%20Aging.%20Social%20Science%20%26amp%3B%20Medicine%2058%3A1985%26%23x2013%3B1997.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2FS0277-9536%2803%2900402-7%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2FS0277-9536%2803%2900402-7%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Cumulative%20biological%20risk%20and%20socio-economic%20differences%20in%20mortality%3A%20MacArthur%20Studies%20of%20Successful%20Aging%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Teresa%20E%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Seeman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eileen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crimmins%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mei-Hua%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Huang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Burton%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Singer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alexander%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bucur%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tara%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gruenewald%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lisa%20F%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Berkman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20B%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Reuben%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%225%5C%2F2004%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2FS0277-9536%2803%2900402-7%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2202779536%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0277953603004027%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A18%3A50Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22HCF2WDQ2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Pinquart%20and%20S%5Cu00f6rensen%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222000%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPinquart%20M%2C%20S%26%23xF6%3Brensen%20S%20%282000%29%20Influences%20of%20socioeconomic%20status%2C%20social%20network%2C%20and%20competence%20on%20subjective%20well-being%20in%20later%20life%3A%20A%20meta-analysis.%20Psychology%20and%20Aging%2015%3A187%26%23x2013%3B224.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1037%5C%2F0882-7974.15.2.187%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1037%5C%2F0882-7974.15.2.187%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Influences%20of%20socioeconomic%20status%2C%20social%20network%2C%20and%20competence%20on%20subjective%20well-being%20in%20later%20life%3A%20A%20meta-analysis.%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Martin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pinquart%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Silvia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00f6rensen%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222000%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1037%5C%2F0882-7974.15.2.187%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221939-1498%2C%200882-7974%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.apa.org%5C%2Fgetdoi.cfm%3Fdoi%3D10.1037%5C%2F0882-7974.15.2.187%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A18%3A43Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22JT22QG53%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Orzack%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-04-21%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BOrzack%20SH%2C%20Stubblefield%20JW%2C%20Akmaev%20VR%2C%20et%20al%20%282015%29%20The%20human%20sex%20ratio%20from%20conception%20to%20birth.%20Proc%20Natl%20Acad%20Sci%20USA%20112%3AE2102%26%23x2013%3BE2111.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1416546112%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1416546112%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20human%20sex%20ratio%20from%20conception%20to%20birth%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Steven%20Hecht%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Orzack%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20William%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stubblefield%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Viatcheslav%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Akmaev%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pere%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Colls%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Santiago%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Munn%5Cu00e9%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Thomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scholl%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Steinsaltz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22James%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zuckerman%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22We%20describe%20the%20trajectory%20of%20the%20human%20sex%20ratio%20from%20conception%20to%20birth%20by%20analyzing%20data%20from%20%28%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20i%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%29%203-%20to%206-d-old%20embryos%2C%20%28%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20ii%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%29%20induced%20abortions%2C%20%28%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20iii%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%29%20chorionic%20villus%20sampling%2C%20%28%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20iv%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%29%20amniocentesis%2C%20and%20%28%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20v%5Cn%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%29%20fetal%20deaths%20and%20live%20births.%20Our%20dataset%20is%20the%20most%20comprehensive%20and%20largest%20ever%20assembled%20to%20estimate%20the%20sex%20ratio%20at%20conception%20and%20the%20sex%20ratio%20trajectory%20and%20is%20the%20first%2C%20to%20our%20knowledge%2C%20to%20include%20all%20of%20these%20types%20of%20data.%20Our%20estimate%20of%20the%20sex%20ratio%20at%20conception%20is%200.5%20%28proportion%20male%29%2C%20which%20contradicts%20the%20common%20claim%20that%20the%20sex%20ratio%20at%20conception%20is%20male-biased.%20The%20sex%20ratio%20among%20abnormal%20embryos%20is%20male-biased%2C%20and%20the%20sex%20ratio%20among%20normal%20embryos%20is%20female-biased.%20These%20biases%20are%20associated%20with%20the%20abnormal%5C%2Fnormal%20state%20of%20the%20sex%20chromosomes%20and%20of%20chromosomes%2015%20and%2017.%20The%20sex%20ratio%20may%20decrease%20in%20the%20first%20week%20or%20so%20after%20conception%20%28due%20to%20excess%20male%20mortality%29%3B%20it%20then%20increases%20for%20at%20least%2010%5Cu201315%20wk%20%28due%20to%20excess%20female%20mortality%29%2C%20levels%20off%20after%20%5Cu223c20%20wk%2C%20and%20declines%20slowly%20from%2028%20to%2035%20wk%20%28due%20to%20excess%20male%20mortality%29.%20Total%20female%20mortality%20during%20pregnancy%20exceeds%20total%20male%20mortality.%20The%20unbiased%20sex%20ratio%20at%20conception%2C%20the%20increase%20in%20the%20sex%20ratio%20during%20the%20first%20trimester%2C%20and%20total%20mortality%20during%20pregnancy%20being%20greater%20for%20females%20are%20fundamental%20insights%20into%20early%20human%20development.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-04-21%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1416546112%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220027-8424%2C%201091-6490%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.pnas.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1416546112%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A06%3A36Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22EG2K9KAT%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Austad%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-04-21%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A3%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAustad%20SN%20%282015%29%20The%20human%20prenatal%20sex%20ratio%3A%20A%20major%20surprise.%20PNAS%20112%3A4839%26%23x2013%3B4840.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1505165112%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1505165112%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20human%20prenatal%20sex%20ratio%3A%20A%20major%20surprise%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Steven%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Austad%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Two%20remarkably%20consistent%20and%20poorly%20understood%20features%20of%20human%20biology%20are%20the%20slightly%20male-biased%20sex%20ratio%20at%20birth%20and%20the%20female%20survival%20advantage%20throughout%20life.%20These%20patterns%20appear%20across%20geography%20and%20time%20wherever%20reliable%20birth%20and%20death%20records%20are%20available%20%281%2C%202%29.%20The%20slight%20male%20bias%2C%20typically%20%5Cu223c51.3%25%20of%20live%20births%2C%20is%20so%20consistent%20%28Fig.%201%20A%20%29%20that%20when%20birth%20sex%20ratios%20deviate%20much%20from%20it%2C%20suspicions%20are%20aroused%20of%20sex-specific%20abortion%20or%20infanticide%20%283%2C%204%29.%20Putting%20together%20the%20birth%20sex%20ratio%20bias%20and%20the%20female%20survival%20advantage%20%285%29%2C%20we%20expect%20a%20monotonically%20declining%20sex%20ratio%20from%20birth%20to%20death%2C%20which%20is%20exactly%20what%20we%20find%20across%20cultures%20and%20across%20historical%20epochs%20%28Fig.%201%20B%20%29.%20By%20age%20100%20y%2C%20there%20are%20three%20to%20four%20women%20for%20every%20surviving%20man%2C%20and%20by%20the%20extraordinary%20age%20of%20110%20y%2C%2095%25%20of%20the%20survivors%20are%20women.%20Note%2C%20however%2C%20that%20until%20later%20life%20the%20sex%20ratio%20does%20not%20stray%20far%20from%2050%3A50%2C%20an%20observation%20that%20would%20gladden%20the%20heart%20of%20evolutionary%20biologist%2C%20Sir%20Ronald%20Fisher%2C%20who%20argued%20that%20natural%20selection%20should%20favor%20equal%20parental%20expenditure%5Cu2014a%20delightfully%20vague%20phrase%5Cu2014in%20males%20and%20females%20%286%29.%20Fisher%20assumed%2C%20as%20have%20many%20since%20then%2C%20that%20the%20human%20sex%20ratio%20at%20conception%20is%20even%20more%20male-biased%20than%20the%20sex%20ratio%20at%20birth%2C%20and%20there%20were%20some%20good%20reasons%20to%20assume%20this.%20First%2C%20males%20are%20less%20likely%20%5Cu2026%20%5Cn%5Cn%5B%5Cu21b5%5D%5B1%5D1Email%3A%20austad%7Bat%7Duab.edu.%5Cn%5Cn%20%5B1%5D%3A%20%23xref-corresp-1-1%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%5C%2F04%5C%2F21%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1505165112%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220027-8424%2C%201091-6490%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.pnas.org%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F112%5C%2F16%5C%2F4839%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A05%3A43Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%2298E6DTMD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Austad%20and%20Fischer%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAustad%20SN%2C%20Fischer%20KE%20%282016%29%20Sex%20Differences%20in%20Lifespan.%20Cell%20Metabolism%2023%3A1022%26%23x2013%3B1033.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.cmet.2016.05.019%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.cmet.2016.05.019%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Sex%20Differences%20in%20Lifespan%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Steven%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Austad%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kathleen%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fischer%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2206%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.cmet.2016.05.019%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2215504131%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS1550413116302376%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T10%3A00%3A37Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%224S3DHHQN%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lema%5Cu00eetre%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222020-03-23%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLema%26%23xEE%3Btre%20J-F%2C%20Ronget%20V%2C%20Tidi%26%23xE8%3Bre%20M%2C%20et%20al%20%282020%29%20Sex%20differences%20in%20adult%20lifespan%20and%20aging%20rates%20of%20mortality%20across%20wild%20mammals.%20Proc%20Natl%20Acad%20Sci%20USA.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1911999117%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1911999117%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Sex%20differences%20in%20adult%20lifespan%20and%20aging%20rates%20of%20mortality%20across%20wild%20mammals%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jean-Fran%5Cu00e7ois%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lema%5Cu00eetre%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Victor%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ronget%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Morgane%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tidi%5Cu00e8re%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dominique%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Allain%5Cu00e9%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V%5Cu00e9rane%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Berger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Aur%5Cu00e9lie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cohas%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fernando%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Colchero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dalia%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Conde%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garratt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andr%5Cu00e1s%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liker%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gabriel%20A.%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Marais%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alexander%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scheuerlein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tam%5Cu00e1s%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sz%5Cu00e9kely%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jean-Michel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gaillard%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22In%20human%20populations%2C%20women%20consistently%20outlive%20men%2C%20which%20suggests%20profound%20biological%20foundations%20for%20sex%20differences%20in%20survival.%20Quantifying%20whether%20such%20sex%20differences%20are%20also%20pervasive%20in%20wild%20mammals%20is%20a%20crucial%20challenge%20in%20both%20evolutionary%20biology%20and%20biogerontology.%20Here%2C%20we%20compile%20demographic%20data%20from%20134%20mammal%20populations%2C%20encompassing%20101%20species%2C%20to%20show%20that%20the%20female%26%23039%3Bs%20median%20lifespan%20is%20on%20average%2018.6%25%20longer%20than%20that%20of%20conspecific%20males%2C%20whereas%20in%20humans%20the%20female%20advantage%20is%20on%20average%207.8%25.%20On%20the%20contrary%2C%20we%20do%20not%20find%20any%20consistent%20sex%20differences%20in%20aging%20rates.%20In%20addition%2C%20sex%20differences%20in%20median%20adult%20lifespan%20and%20aging%20rates%20are%20both%20highly%20variable%20across%20species.%20Our%20analyses%20suggest%20that%20the%20magnitude%20of%20sex%20differences%20in%20mammalian%20mortality%20patterns%20is%20likely%20shaped%20by%20local%20environmental%20conditions%20in%20interaction%20with%20the%20sex-specific%20costs%20of%20sexual%20selection.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22Mar%2023%2C%202020%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22eng%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1073%5C%2Fpnas.1911999117%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221091-6490%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-30T09%3A47%3A09Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22B6QAFUMT%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Zanoboni%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%221976-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BZanoboni%20A%2C%20Schwarz%20D%2C%20Zanoboni-Muciaccia%20W%20%281976%29%20Stimulation%20of%20insulin%20secretion%20in%20man%20by%20oral%20glycerol%20administration.%20Metab%20Clin%20Exp%2025%3A41%26%23x2013%3B45.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2F0026-0495%2876%2990158-x%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2F0026-0495%2876%2990158-x%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Stimulation%20of%20insulin%20secretion%20in%20man%20by%20oral%20glycerol%20administration%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zanoboni%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schwarz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zanoboni-Muciaccia%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20effects%20of%20an%20orally%20administered%20glycerol%20load%20%281%20g%5C%2FKg%20body%20weight%29%20on%20blood%20glucose%2C%20plasma%20FFA%2C%20and%20plasma%20insulin%20levels%20have%20been%20determined%20in%20eight%20normal%20fasting%20or%20glucose%20loaded%20%281%20g%5C%2FKg%20body%20weight%29%20volunteers.%20Blood%20glucose%20levels%20were%20not%20affected%20by%20glycerol%20loading%20while%20glicemia%20followed%20the%20same%20pattern%20of%20a%20glucose%20tolerance%20test%20in%20the%20group%20treated%20with%20glucose%20plus%20glycerol.%20Plasma%20FFA%20were%20significantly%20lowered%20only%2090%20min%20after%20glycerol%20loading%20while%20they%20had%20markedly%20and%20persistently%20decreased%20by%20glycerol%20plus%20glucose%20per%20os.%20Finally%2C%20though%20glicemia%20did%20not%20change%2C%20insulinemia%20was%20markedly%20increased%20by%20glycereol%2C%2090%20min%20after%20loading%3B%20moreover%2C%20plasma%20IRI%20was%20significantly%20higher%20in%20the%20group%20treated%20with%20glycerol%20plus%20glucose%20than%20in%20the%20group%20treated%20with%20glucose%20alone.%20These%20data%20suggest%20that%20the%20release%20of%20insulin%20may%20be%20stimulated%20by%20a%20very%20small%20increment%20of%20blood%20glucose%2C%20which%20derives%20from%20glycerol.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22Jan%201976%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22eng%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2F0026-0495%2876%2990158-x%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220026-0495%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%226ZD5MYAL%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-29T14%3A53%3A22Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22KC29XC9H%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAssociation%20of%20Triglyceride-Lowering%20LPL%20Variants%20and%20LDL-C%26%23x2013%3BLowering%20LDLR%20Variants%20With%20Risk%20of%20Coronary%20Heart%20Disease%20%7C%20Cardiology%20%7C%20JAMA%20%7C%20JAMA%20Network.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjamanetwork.com%5C%2Fjournals%5C%2Fjama%5C%2Farticle-abstract%5C%2F2722770%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjamanetwork.com%5C%2Fjournals%5C%2Fjama%5C%2Farticle-abstract%5C%2F2722770%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2029%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Association%20of%20Triglyceride-Lowering%20LPL%20Variants%20and%20LDL-C%5Cu2013Lowering%20LDLR%20Variants%20With%20Risk%20of%20Coronary%20Heart%20Disease%20%7C%20Cardiology%20%7C%20JAMA%20%7C%20JAMA%20Network%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjamanetwork.com%5C%2Fjournals%5C%2Fjama%5C%2Farticle-abstract%5C%2F2722770%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-29T10%3A39%3A29Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22N98JYWCU%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Madsen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222008%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BMadsen%20EL%2C%20Rissanen%20A%2C%20Bruun%20JM%2C%20et%20al%20%282008%29%20Weight%20loss%20larger%20than%2010%25%20is%20needed%20for%20general%20improvement%20of%20levels%20of%20circulating%20adiponectin%20and%20markers%20of%20inflammation%20in%20obese%20subjects%3A%20a%203-year%20weight%20loss%20study.%20European%20Journal%20of%20Endocrinology%20158%3A179%26%23x2013%3B187.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1530%5C%2FEJE-07-0721%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1530%5C%2FEJE-07-0721%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Weight%20loss%20larger%20than%2010%25%20is%20needed%20for%20general%20improvement%20of%20levels%20of%20circulating%20adiponectin%20and%20markers%20of%20inflammation%20in%20obese%20subjects%3A%20a%203-year%20weight%20loss%20study%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Erik%20L%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Madsen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Aila%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rissanen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jens%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bruun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kristin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Skogstrand%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Serena%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tonstad%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hougaard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bj%5Cu00f8rn%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Richelsen%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Objective%3A%20To%20investigate%20the%20effects%20of%3A%20I%29%20short-%20%288%20weeks%29%2C%20II%29%20long-term%20%283%20years%29%20weight%20loss%2C%20and%20III%29%20the%20degree%20of%20weight%20loss%20on%20circulating%20levels%20of%20adiponectin%2C%20high%20sensitive-C%20reactive%20protein%20%28hs-CRP%29%2C%20and%20%5Cufb01brinogen%20in%20obese%20subjects.%20Moreover%2C%20to%20evaluate%20the%20effect%20of%20the%20lipase%20inhibitor%2C%20orlistat%2C%20on%20these%20parameters.%20Design%3A%20Weight%20loss%20induced%20in%2093%20obese%20subjects%20%28mean%20weight%3A%20108.9G15.8%20kg%29%20through%208-week%20very-low-energy%20diet%20%28VLED%2C%20800%20kcal%5C%2Fday%29%20followed%20by%20randomization%20to%20orlistat%20or%20placebo%20together%20with%20lifestyle%20intervention%20for%20further%203%20years.%20Adiponectin%20and%20hs-CRP%20were%20measured%20at%20baseline%2C%20after%208%20weeks%20of%20VLED%20and%206%2C%2012%2C%20and%2036%20months%20after%20the%20VLED%20by%20%5Cufb02owmetric%20xMAP%20technology%20%28Luminex%20Multi-Analyte%20Pro%5Cufb01ling%20System%2C%20Luminex%20Corp.%2C%20Austin%2C%20TX%2C%20USA%29.%20Fibrinogen%20was%20measured%20in%20a%20coagulation%20assay.%5CnResults%3A%20Weight%20loss%20after%20VLED%20treatment%20was%2014.3G4.5%20kg%20and%20after%203%20years%207.7G8.7%20kg.%20Orlistattreated%20subjects%20regained%203.9%20kg%20less%20than%20placebo-treated%20from%20the%20end%20of%20the%20VLED%20to%203%20years%20%28PZ0.01%29.%20No%20differences%20were%20detected%20between%20the%20two%20groups%20regarding%20changes%20in%20adiponectin%2C%20hs-CRP%2C%20or%20%5Cufb01brinogen.%20Accordingly%2C%20the%20groups%20were%20combined%20for%20further%20analyses.%20Serum%20adiponectin%20increased%20by%2022%25%20%28P%210.05%29%20after%20the%20VLED%20but%20returned%20to%20baseline%20after%203%20years.%20Both%20short-%20and%20long-term%20weight%20losses%20needed%20to%20be%20in%20excess%20of%2010%25%20%28w12%20kg%29%20in%20order%20to%20increase%20adiponectin%20levels%20signi%5Cufb01cantly.%20Weight%20loss%20was%20associated%20with%20a%20signi%5Cufb01cant%20decrease%20in%20hs-CRP.%20Fibrinogen%20decreased%20by%2012%25%20%28P%210.05%29%20after%203%20years.%5CnConclusions%3A%20In%20obese%20subjects%2C%20weight%20loss%20was%20associated%20with%20an%20increase%20in%20serum%20adiponectin%20and%20a%20decrease%20in%20hs-CRP%20and%20plasma%20%5Cufb01brinogen.%20Long-term%20weight%20loss%20%283%20years%29%20must%20exceed%2010%25%20to%20induce%20a%20combined%20signi%5Cufb01cant%20improvement%20in%20these%20in%5Cufb02ammatory%20markers.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2202%5C%2F2008%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1530%5C%2FEJE-07-0721%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220804-4643%2C%201479-683X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Feje.bioscientifica.com%5C%2Fview%5C%2Fjournals%5C%2Feje%5C%2F158%5C%2F2%5C%2F179.xml%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T18%3A25%3A24Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22ZAHCKML2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Danesh%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222000-07-22%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A3%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BDanesh%20J%2C%20Whincup%20P%2C%20Walker%20M%2C%20et%20al%20%282000%29%20Low%20grade%20inflammation%20and%20coronary%20heart%20disease%3A%20prospective%20study%20and%20updated%20meta-analyses.%20BMJ%20321%3A199%26%23x2013%3B204.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1136%5C%2Fbmj.321.7255.199%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1136%5C%2Fbmj.321.7255.199%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Low%20grade%20inflammation%20and%20coronary%20heart%20disease%3A%20prospective%20study%20and%20updated%20meta-analyses%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22John%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Danesh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Peter%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Whincup%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mary%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Walker%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lucy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lennon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrew%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Thomson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Appleby%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20Ruth%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gallimore%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mark%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pepys%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Objective%3A%20To%20assess%20associations%20between%20baseline%20values%20of%20four%20different%20circulating%20markers%20of%20inflammation%20and%20future%20risk%20of%20coronary%20heart%20disease%2C%20potential%20triggers%20of%20systemic%20inflammation%20%28such%20as%20persistent%20infection%29%2C%20and%20other%20markers%20of%20inflammation.%5CnDesign%3A%20Nested%20case-control%20comparisons%20in%20a%20prospective%2C%20population%20based%20cohort.%5CnSetting%3A%20General%20practices%20in%2018%20towns%20in%20Britain.%5CnParticipants%3A%20506%20men%20who%20died%20from%20coronary%20heart%20disease%20or%20had%20a%20non-fatal%20myocardial%20infarction%20and%201025%20men%20who%20remained%20free%20of%20such%20disease%20until%201996%20selected%20from%205661%20men%20aged%2040%5Cu201359%20years%20who%20provided%20blood%20samples%20in%201978-1980.%5CnMain%20outcome%20measures%3A%20Plasma%20concentrations%20of%20C%20reactive%20protein%2C%20serum%20amyloid%20A%20protein%2C%20and%20serum%20albumin%20and%20leucocyte%20count.%20Information%20on%20fatal%20and%20non-fatal%20coronary%20heart%20disease%20was%20obtained%20from%20medical%20records%20and%20death%20certificates.%5CnResults%3A%20Compared%20with%20men%20in%20the%20bottom%20third%20of%20baseline%20measurements%20of%20C%20reactive%20protein%2C%20men%20in%20the%20top%20third%20had%20an%20odds%20ratio%20for%20coronary%20heart%20disease%20of%202.13%20%2895%25%20confidence%20interval%201.38%20to%203.28%29%20after%20age%2C%20town%2C%20smoking%2C%20vascular%20risk%20factors%2C%20and%20indicators%20of%20socioeconomic%20status%20were%20adjusted%20for.%20Similar%20adjusted%20odds%20ratios%20were%201.65%20%281.07%20to%202.55%29%20for%20serum%20amyloid%20A%20protein%3B%201.12%20%280.71%20to%201.77%29%20for%20leucocyte%20count%3B%20and%200.67%20%280.43%20to%201.04%29%20for%20albumin.%20No%20strong%20associations%20were%20observed%20of%20these%20factors%20with%20Helicobacter%20pylori%20seropositivity%2C%20Chlamydia%20pneumoniae%20IgG%20titres%2C%20or%20plasma%20total%20homocysteine%20concentrations.%20Baseline%20values%20of%20the%20acute%20phase%20reactants%20were%20significantly%20associated%20with%20one%20another%20%28P%26lt%3B0.0001%29%2C%20although%20the%20association%20between%20low%20serum%20albumin%20concentration%20and%20leucocyte%20count%20was%20weaker%20%28P%3D0.08%29.%5CnConclusion%3A%20In%20the%20context%20of%20results%20from%20other%20relevant%20studies%20these%20findings%20suggest%20that%20some%20inflammatory%20processes%2C%20unrelated%20to%20the%20chronic%20infections%20studied%20here%2C%20are%20likely%20to%20be%20involved%20in%20coronary%20heart%20disease.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222000%5C%2F07%5C%2F22%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1136%5C%2Fbmj.321.7255.199%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220959-8138%2C%201468-5833%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.bmj.com%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F321%5C%2F7255%5C%2F199%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T18%3A13%3A11Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BZZFC7M4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Nguyen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010-09-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BNguyen%20NT%2C%20Nguyen%20X-MT%2C%20Wooldridge%20JB%2C%20et%20al%20%282010%29%20Association%20of%20obesity%20with%20risk%20of%20coronary%20heart%20disease%3A%20findings%20from%20the%20National%20Health%20and%20Nutrition%20Examination%20Survey%2C%201999%26%23x2013%3B2006.%20Surgery%20for%20Obesity%20and%20Related%20Diseases%206%3A465%26%23x2013%3B469.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.soard.2010.02.038%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.soard.2010.02.038%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Association%20of%20obesity%20with%20risk%20of%20coronary%20heart%20disease%3A%20findings%20from%20the%20National%20Health%20and%20Nutrition%20Examination%20Survey%2C%201999%5Cu20132006%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ninh%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xuan-Mai%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22James%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wooldridge%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Johnathan%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Slone%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22John%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lane%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Background%5CnObesity%20is%20a%20well-known%20risk%20factor%20for%20the%20development%20of%20coronary%20heart%20disease%20%28CHD%29.%20The%20aim%20of%20the%20present%20study%20was%20to%20examine%20the%20differences%20in%20the%2010-year%20CHD%20risk%20with%20increasing%20severity%20of%20obesity%20in%20men%20and%20women%20participating%20in%20the%20latest%20National%20Health%20and%20Nutrition%20Examination%20Survey.%5CnMethods%5CnData%20from%20a%20representative%20sample%20of%2012%2C500%20U.S.%20participants%20in%20the%20National%20Health%20and%20Nutrition%20Examination%20Survey%20from%201999%20to%202006%20were%20reviewed.%20The%20Framingham%20risk%20score%20was%20calculated%20for%20men%20and%20women%20according%20to%20a%20body%20mass%20index%20%28BMI%29%20of%20%26lt%3B25.0%2C%2025.0%5Cu201329.9%2C%2030.0%5Cu201334.9%2C%20and%20%5Cu226535.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2.%5CnResults%5CnThe%20prevalence%20of%20those%20with%20hypertension%20increased%20with%20an%20increasing%20BMI%2C%20from%2024%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20%26lt%3B25.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2%20to%2054%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20of%20%5Cu226535.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2.%20The%20prevalence%20of%20an%20abnormal%20total%20cholesterol%20level%20%28%26gt%3B200%20mg%5C%2FdL%29%20increased%20from%2040%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20%26lt%3B25.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2%20to%2048%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20of%20%5Cu226535.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2.%20The%2010-year%20CHD%20risk%20for%20men%20increased%20from%203.1%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20%26lt%3B25.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2%20to%20a%20peak%20of%205.6%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20of%2030.0%5Cu201334.9%20kg%5C%2Fm2.%20The%2010-year%20CHD%20risk%20for%20women%20increased%20from%20.8%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20%26lt%3B25.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2%20to%20a%20peak%20of%201.5%25%20for%20a%20BMI%20of%20%5Cu226535.0%20kg%5C%2Fm2.%20Both%20diabetes%20and%20hypertension%20were%20independent%20risk%20factors%20for%20an%20increasing%20CHD%20risk.%5CnConclusions%5CnThe%2010-year%20CHD%20risk%2C%20calculated%20using%20the%20Framingham%20risk%20score%2C%20substantially%20increased%20with%20an%20increasing%20BMI.%20An%20important%20implication%20from%20our%20findings%20is%20the%20need%20to%20implement%20surgical%20and%20medical%20approaches%20to%20weight%20reduction%20to%20reduce%20the%20effect%20of%20morbidity%20and%20mortality%20from%20CHD%20on%20the%20U.S.%20healthcare%20system.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22September%201%2C%202010%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.soard.2010.02.038%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221550-7289%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS155072891000078X%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T18%3A06%3A04Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%226QAPJYLP%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Partsalaki%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPartsalaki%20I%2C%20Karvela%20A%2C%20Spiliotis%20BE%20%282012%29%20Metabolic%20impact%20of%20a%20ketogenic%20diet%20compared%20to%20a%20hypocaloric%20diet%20in%20obese%20children%20and%20adolescents.%20J%20Pediatr%20Endocrinol%20Metab%2025%3A697%26%23x2013%3B704.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1515%5C%2Fjpem-2012-0131%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1515%5C%2Fjpem-2012-0131%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Metabolic%20impact%20of%20a%20ketogenic%20diet%20compared%20to%20a%20hypocaloric%20diet%20in%20obese%20children%20and%20adolescents%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ioanna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Partsalaki%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alexia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Karvela%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bessie%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spiliotis%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22BACKGROUND%3A%20The%20effects%20of%20carbohydrate-restricted%20%28ketogenic%29%20diets%20on%20metabolic%20parameters%20in%20children%20have%20been%20incompletely%20assessed.%5CnOBJECTIVE%3A%20To%20compare%20the%20efficacy%20and%20metabolic%20impact%20of%20ketogenic%20and%20hypocaloric%20diets%20in%20obese%20children%20and%20adolescents.%5CnSUBJECTS%3A%20Fifty-eight%20obese%20subjects%20were%20placed%20on%20one%20of%20the%20two%20diets%20for%206%20months.%5CnMETHODS%3A%20Anthropometric%20measurements%2C%20body%20composition%2C%20oral%20glucose%5C%2Finsulin%20tolerance%20test%2C%20lipidemic%20profile%2C%20high%20molecular%20weight%20%28HMW%29%20adiponectin%2C%20whole-body%20insulin%20sensitivity%20index%20%28WBISI%29%2C%20and%20homeostatic%20model%20assessment-insulin%20resistance%20%28HOMA-IR%29%20were%20determined%20before%20and%20after%20each%20diet.%5CnRESULTS%3A%20Both%20groups%20significantly%20reduced%20their%20weight%2C%20fat%20mass%2C%20waist%20circumference%2C%20fasting%20insulin%2C%20and%20HOMA-IR%20%28p%20%3D%200.009%20for%20ketogenic%20and%20p%20%3D%200.014%20for%20hypocaloric%29%2C%20but%20the%20differences%20were%20greater%20in%20the%20ketogenic%20group.%20Both%20groups%20increased%20WBISI%20significantly%2C%20but%20only%20the%20ketogenic%20group%20increased%20HMW%20adiponectin%20significantly%20%28p%20%3D%200.025%29.%5CnCONCLUSIONS%3A%20The%20ketogenic%20diet%20revealed%20more%20pronounced%20improvements%20in%20weight%20loss%20and%20metabolic%20parameters%20than%20the%20hypocaloric%20diet%20and%20may%20be%20a%20feasible%20and%20safe%20alternative%20for%20children%26%23039%3Bs%20weight%20loss.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22eng%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1515%5C%2Fjpem-2012-0131%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220334-018X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T18%3A01%3A30Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%2269H39AXY%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Volek%20et%20al.%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BVolek%20J%2C%20Phinney%20S%2C%20Forsythe%20C%2C%20et%20al%20%283%29%20%28PDF%29%20Carbohydrate%20Restriction%20has%20a%20More%20Favorable%20Impact%20on%20the%20Metabolic%20Syndrome%20than%20a%20Low%20Fat%20Diet.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.researchgate.net%5C%2Fpublication%5C%2F23663658_Carbohydrate_Restriction_has_a_More_Favorable_Impact_on_the_Metabolic_Syndrome_than_a_Low_Fat_Diet%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.researchgate.net%5C%2Fpublication%5C%2F23663658_Carbohydrate_Restriction_has_a_More_Favorable_Impact_on_the_Metabolic_Syndrome_than_a_Low_Fat_Diet%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2026%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22%283%29%20%28PDF%29%20Carbohydrate%20Restriction%20has%20a%20More%20Favorable%20Impact%20on%20the%20Metabolic%20Syndrome%20than%20a%20Low%20Fat%20Diet%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Volek%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stephen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Phinney%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cassandra%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Forsythe%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Erin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Quinn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wood%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Puglisi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22William%20J%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kraemer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Doug%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bibus%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Maria%20Luz%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fernandez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20D%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Feinman%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.researchgate.net%5C%2Fpublication%5C%2F23663658_Carbohydrate_Restriction_has_a_More_Favorable_Impact_on_the_Metabolic_Syndrome_than_a_Low_Fat_Diet%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TX7VNSFI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T17%3A58%3A42Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22S7I9MHTC%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BKeto%20Longevity%20Webinar.%20In%3A%20Google%20Docs.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdocs.google.com%5C%2Fdocument%5C%2Fu%5C%2F1%5C%2Fd%5C%2F1uD7YzT94lPqTYB00DGyKEDuQNjp0TOKKGv5d1s6dbdI%5C%2Fedit%3Fusp%3Dsharing%26amp%3Busp%3Dembed_facebook%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdocs.google.com%5C%2Fdocument%5C%2Fu%5C%2F1%5C%2Fd%5C%2F1uD7YzT94lPqTYB00DGyKEDuQNjp0TOKKGv5d1s6dbdI%5C%2Fedit%3Fusp%3Dsharing%26amp%3Busp%3Dembed_facebook%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2026%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Keto%20Longevity%20Webinar%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Title%3A%20Can%20You%20Extend%20Your%20Lifespan%20With%20a%20Ketogenic%20Diet%3F%20%20Intro%3A%20The%20Guaranteed%20Ketogenic%20Diet%20%20Part%201%3A%20How%20Long%20Can%20You%20Expect%20to%20Live%3F%20How%20long%20does%20the%20average%20person%20live%3F%20-%20Erin%20Gender%20differences%20Location%20How%20much%20influenced%20by%20diet%20itself%3F%20Socioeconomic%3F%20How%20much%20can%20we%20impact%3F%20Genetics%3F...%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdocs.google.com%5C%2Fdocument%5C%2Fu%5C%2F1%5C%2Fd%5C%2F1uD7YzT94lPqTYB00DGyKEDuQNjp0TOKKGv5d1s6dbdI%5C%2Fedit%3Fusp%3Dsharing%26usp%3Dembed_facebook%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en-GB%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T17%3A28%3A14Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22W7HE8HHJ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Wilson%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222005-11-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BWilson%20PWF%2C%20D%26%23x2019%3BAgostino%20RB%2C%20Parise%20H%2C%20et%20al%20%282005%29%20Metabolic%20Syndrome%20as%20a%20Precursor%20of%20Cardiovascular%20Disease%20and%20Type%202%20Diabetes%20Mellitus.%20Circulation%20112%3A3066%26%23x2013%3B3072.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1161%5C%2FCIRCULATIONAHA.105.539528%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1161%5C%2FCIRCULATIONAHA.105.539528%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Metabolic%20Syndrome%20as%20a%20Precursor%20of%20Cardiovascular%20Disease%20and%20Type%202%20Diabetes%20Mellitus%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Peter%20W.F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wilson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ralph%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22D%5Cu2019Agostino%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Helen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Parise%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lisa%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sullivan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22James%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Meigs%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222005-11-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1161%5C%2FCIRCULATIONAHA.105.539528%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220009-7322%2C%201524-4539%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ahajournals.org%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1161%5C%2FCIRCULATIONAHA.105.539528%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T17%3A09%3A36Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22T65RIIYX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gershuni%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222018-09-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BGershuni%20VM%2C%20Yan%20SL%2C%20Medici%20V%20%282018%29%20Nutritional%20Ketosis%20for%20Weight%20Management%20and%20Reversal%20of%20Metabolic%20Syndrome.%20Curr%20Nutr%20Rep%207%3A97%26%23x2013%3B106.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs13668-018-0235-0%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs13668-018-0235-0%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Nutritional%20Ketosis%20for%20Weight%20Management%20and%20Reversal%20of%20Metabolic%20Syndrome%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Victoria%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gershuni%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stephanie%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Valentina%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Medici%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20goal%20of%20this%20paper%20is%20to%20review%20current%20literature%20on%20nutritional%20ketosis%20within%20the%20context%20of%20weight%20management%20and%20metabolic%20syndrome%2C%20namely%2C%20insulin%20resistance%2C%20lipid%20profile%2C%20cardiovascular%20disease%20risk%2C%20and%20development%20of%20non-alcoholic%20fatty%20liver%20disease.%20We%20provide%20background%20on%20the%20mechanism%20of%20ketogenesis%20and%20describe%20nutritional%20ketosis.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222018-09-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs13668-018-0235-0%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222161-3311%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs13668-018-0235-0%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%226GWVSRHP%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-26T16%3A54%3A11Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%226NT2M8NW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Volek%20and%20Sharman%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222004%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BVolek%20JS%2C%20Sharman%20MJ%20%282004%29%20Cardiovascular%20and%20Hormonal%20Aspects%20of%20Very-Low-Carbohydrate%20Ketogenic%20Diets.%20Obesity%20Research%2012%3A115S-123S.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Foby.2004.276%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Foby.2004.276%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Cardiovascular%20and%20Hormonal%20Aspects%20of%20Very-Low-Carbohydrate%20Ketogenic%20Diets%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeff%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Volek%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Matthew%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sharman%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22VOLEK%2C%20JEFF%20S.%20AND%20MATTHEW%20J.%20SHARMAN.%20Cardiovascular%20and%20hormonal%20aspects%20of%20very-lowcarbohydrate%20ketogenic%20diets.%20Obes%20Res.%202004%3B12%3A%20115S%5Cu2013123S.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2211%5C%2F2004%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1038%5C%2Foby.2004.276%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2210717323%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Foby.2004.276%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T17%3A34%3A29Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%223BUZRYYF%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Kosinski%20and%20Jornayvaz%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222017-05-19%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BKosinski%20C%2C%20Jornayvaz%20F%20%282017%29%20Effects%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20on%20Cardiovascular%20Risk%20Factors%3A%20Evidence%20from%20Animal%20and%20Human%20Studies.%20Nutrients%209%3A517.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fnu9050517%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fnu9050517%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effects%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20on%20Cardiovascular%20Risk%20Factors%3A%20Evidence%20from%20Animal%20and%20Human%20Studies%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christophe%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kosinski%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fran%5Cu00e7ois%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Jornayvaz%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20treatment%20of%20obesity%20and%20cardiovascular%20diseases%20is%20one%20of%20the%20most%20dif%5Cufb01cult%20and%20important%20challenges%20nowadays.%20Weight%20loss%20is%20frequently%20offered%20as%20a%20therapy%20and%20is%20aimed%20at%20improving%20some%20of%20the%20components%20of%20the%20metabolic%20syndrome.%20Among%20various%20diets%2C%20ketogenic%20diets%2C%20which%20are%20very%20low%20in%20carbohydrates%20and%20usually%20high%20in%20fats%20and%5C%2For%20proteins%2C%20have%20gained%20in%20popularity.%20Results%20regarding%20the%20impact%20of%20such%20diets%20on%20cardiovascular%20risk%20factors%20are%20controversial%2C%20both%20in%20animals%20and%20humans%2C%20but%20some%20improvements%20notably%20in%20obesity%20and%20type%202%20diabetes%20have%20been%20described.%20Unfortunately%2C%20these%20effects%20seem%20to%20be%20limited%20in%20time.%20Moreover%2C%20these%20diets%20are%20not%20totally%20safe%20and%20can%20be%20associated%20with%20some%20adverse%20events.%20Notably%2C%20in%20rodents%2C%20development%20of%20nonalcoholic%20fatty%20liver%20disease%20%28NAFLD%29%20and%20insulin%20resistance%20have%20been%20described.%20The%20aim%20of%20this%20review%20is%20to%20discuss%20the%20role%20of%20ketogenic%20diets%20on%20different%20cardiovascular%20risk%20factors%20in%20both%20animals%20and%20humans%20based%20on%20available%20evidence.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222017-05-19%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fnu9050517%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222072-6643%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F2072-6643%5C%2F9%5C%2F5%5C%2F517%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%229P7SYM5Z%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T17%3A25%3A20Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QYCRY2WY%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rusek%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222019-08-09%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BRusek%20M%2C%20Pluta%20R%2C%20U%26%23x142%3Bamek-Kozio%26%23x142%3B%20M%2C%20Czuczwar%20SJ%20%282019%29%20Ketogenic%20Diet%20in%20Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease.%20IJMS%2020%3A3892.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijms20163892%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijms20163892%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Ketogenic%20Diet%20in%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20Disease%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Marta%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rusek%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ryszard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pluta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Marzena%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22U%5Cu0142amek-Kozio%5Cu0142%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stanis%5Cu0142aw%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Czuczwar%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22At%20present%2C%20the%20prevalence%20of%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease%2C%20a%20devastating%20neurodegenerative%20disorder%2C%20is%20increasing.%20Although%20the%20mechanism%20of%20the%20underlying%20pathology%20is%20not%20fully%20uncovered%2C%20in%20the%20last%20years%2C%20there%20has%20been%20signi%5Cufb01cant%20progress%20in%20its%20understanding.%20This%20includes%3A%20Progressive%20deposition%20of%20amyloid%20%5Cu03b2-peptides%20in%20amyloid%20plaques%20and%20hyperphosphorylated%20tau%20protein%20in%20intracellular%20as%20neuro%5Cufb01brillary%20tangles%3B%20neuronal%20loss%3B%20and%20impaired%20glucose%20metabolism.%20Due%20to%20a%20lack%20of%20e%5Cufb00ective%20prevention%20and%20treatment%20strategy%2C%20emerging%20evidence%20suggests%20that%20dietary%20and%20metabolic%20interventions%20could%20potentially%20target%20these%20issues.%20The%20ketogenic%20diet%20is%20a%20very%20high-fat%2C%20low-carbohydrate%20diet%2C%20which%20has%20a%20fasting-like%20e%5Cufb00ect%20bringing%20the%20body%20into%20a%20state%20of%20ketosis.%20The%20presence%20of%20ketone%20bodies%20has%20a%20neuroprotective%20impact%20on%20aging%20brain%20cells.%20Moreover%2C%20their%20production%20may%20enhance%20mitochondrial%20function%2C%20reduce%20the%20expression%20of%20in%5Cufb02ammatory%20and%20apoptotic%20mediators.%20Thus%2C%20it%20has%20gained%20interest%20as%20a%20potential%20therapy%20for%20neurodegenerative%20disorders%20like%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease.%20This%20review%20aims%20to%20examine%20the%20role%20of%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%20in%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease%20progression%20and%20to%20outline%20speci%5Cufb01c%20aspects%20of%20the%20nutritional%20pro%5Cufb01le%20providing%20a%20rationale%20for%20the%20implementation%20of%20dietary%20interventions%20as%20a%20therapeutic%20strategy%20for%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222019-08-09%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fijms20163892%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221422-0067%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F1422-0067%5C%2F20%5C%2F16%5C%2F3892%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22SPT2NJ53%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T17%3A15%3A25Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BNDJSCA5%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22W%5Cu0142odarek%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222019-01-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BW%26%23x142%3Bodarek%20D%20%282019%29%20Role%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20in%20Neurodegenerative%20Diseases%20%28Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease%20and%20Parkinson%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease%29.%20Nutrients%2011%3A169.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fnu11010169%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fnu11010169%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Role%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20in%20Neurodegenerative%20Diseases%20%28Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20Disease%20and%20Parkinson%5Cu2019s%20Disease%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dariusz%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22W%5Cu0142odarek%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20goal%20of%20this%20review%20was%20to%20assess%20the%20effectiveness%20of%20ketogenic%20diets%20on%20the%20therapy%20of%20neurodegenerative%20diseases.%20The%20ketogenic%20diet%20is%20a%20low-carbohydrate%20and%20fat-rich%20diet.%20Its%20implementation%20has%20a%20fasting-like%20effect%2C%20which%20brings%20the%20body%20into%20a%20state%20of%20ketosis.%20The%20ketogenic%20diet%20has%2C%20for%20almost%20100%20years%2C%20been%20used%20in%20the%20therapy%20of%20drug-resistant%20epilepsy%2C%20but%20current%20studies%20indicate%20possible%20neuroprotective%20effects.%20Thus%20far%2C%20only%20a%20few%20studies%20have%20evaluated%20the%20role%20of%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%20in%20the%20prevention%20of%20Parkinson%5Cu2019s%20disease%20%28PD%29%20and%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease%20%28AD%29.%20Single%20studies%20with%20human%20participants%20have%20demonstrated%20a%20reduction%20of%20disease%20symptoms%20after%20application.%20The%20application%20of%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%20to%20elderly%20people%2C%20however%2C%20raises%20certain%20concerns.%20Persons%20with%20neurodegenerative%20diseases%20are%20at%20risk%20of%20malnutrition%2C%20while%20food%20intake%20reduction%20is%20associated%20with%20disease%20symptoms.%20In%20turn%2C%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%20leads%20to%20a%20reduced%20appetite%3B%20it%20is%20not%20attractive%20from%20an%20organoleptic%20point%20of%20view%2C%20and%20may%20be%20accompanied%20by%20side%20effects%20of%20the%20gastrointestinal%20system.%20All%20this%20may%20lead%20to%20further%20lowering%20of%20consumed%20food%20portions%20by%20elderly%20persons%20with%20neurodegenerative%20diseases%20and%2C%20in%20consequence%2C%20to%20further%20reduction%20in%20the%20supply%20of%20nutrients%20provided%20by%20the%20diet.%20Neither%20data%20on%20the%20long-term%20application%20of%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%20in%20patients%20with%20neurodegenerative%20disease%20or%20data%20on%20its%20effects%20on%20disease%20symptoms%20are%20available.%20Further%20research%20is%20needed%20to%20evaluate%20the%20suitability%20of%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%20in%20the%20therapy%20of%20AD-%20or%20PD-affected%20persons.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222019-01-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fnu11010169%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222072-6643%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F2072-6643%5C%2F11%5C%2F1%5C%2F169%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22SPT2NJ53%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T17%3A07%3A06Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22Q6VKADKU%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BRole%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20in%20Neurodegenerative%20Diseases%20%28Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease%20and%20Parkinson%26%23x2019%3Bs%20Disease%29.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC6356942%5C%2F%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC6356942%5C%2F%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2019%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Role%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20in%20Neurodegenerative%20Diseases%20%28Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20Disease%20and%20Parkinson%5Cu2019s%20Disease%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC6356942%5C%2F%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T17%3A01%3A10Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228YKAEID7%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Fine%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BFine%20E%20Targeting%20insulin%20inhibition%20as%20a%20metabolic%20therapy%20in%20advanced%20cancer%3A%20a%20pilot%20safety%20and%20feasibility%20dietary%20trial%20in%2010%20patients.%20-%20PubMed%20-%20NCBI.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F22840388%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F22840388%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2019%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Targeting%20insulin%20inhibition%20as%20a%20metabolic%20therapy%20in%20advanced%20cancer%3A%20a%20pilot%20safety%20and%20feasibility%20dietary%20trial%20in%2010%20patients.%20-%20PubMed%20-%20NCBI%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fine%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F22840388%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A57%3A25Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%229EYTNPQ2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Zhou%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BZhou%20W%20The%20calorically%20restricted%20ketogenic%20diet%2C%20an%20effective%20alternative%20therapy%20for%20malignant%20brain%20cancer.%20-%20PubMed%20-%20NCBI.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F17313687%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F17313687%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2019%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20calorically%20restricted%20ketogenic%20diet%2C%20an%20effective%20alternative%20therapy%20for%20malignant%20brain%20cancer.%20-%20PubMed%20-%20NCBI%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhou%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F17313687%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A51%3A30Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22Q7HKJ46T%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Klement%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BKlement%20Anti-Tumor%20Effects%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20in%20Mice%3A%20A%20Meta-Analysis.%20-%20PubMed%20-%20NCBI.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F27159218%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F27159218%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2019%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Anti-Tumor%20Effects%20of%20Ketogenic%20Diets%20in%20Mice%3A%20A%20Meta-Analysis.%20-%20PubMed%20-%20NCBI%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Klement%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpubmed%5C%2F27159218%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A45%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22LBX53LKX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Kentaro%20Nakamura%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222018-02-14%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BKentaro%20Nakamura%2C%20Hidekazu%20Tonouchi%2C%20Akina%20Sasayama%2C%20Kinya%20Ashida%20%282018%29%20A%20Ketogenic%20Formula%20Prevents%20Tumor%20Progression%20and%20Cancer%20Cachexia%20by%20Attenuating%20Systemic%20Inflammation%20in%20Colon%2026%20Tumor-Bearing%20Mice.%20Nutrients%2010%3A206.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fnu10020206%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fnu10020206%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20Ketogenic%20Formula%20Prevents%20Tumor%20Progression%20and%20Cancer%20Cachexia%20by%20Attenuating%20Systemic%20Inflammation%20in%20Colon%2026%20Tumor-Bearing%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22name%22%3A%22Kentaro%20Nakamura%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22name%22%3A%22Hidekazu%20Tonouchi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22name%22%3A%22Akina%20Sasayama%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22name%22%3A%22Kinya%20Ashida%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Low-carbohydrate%2C%20high-fat%20diets%20%28ketogenic%20diets%29%20might%20prevent%20tumor%20progression%20and%20could%20be%20used%20as%20supportive%20therapy%3B%20however%2C%20few%20studies%20have%20addressed%20the%20effect%20of%20such%20diets%20on%20colorectal%20cancer.%20An%20infant%20formula%20with%20a%20ketogenic%20composition%20%28ketogenic%20formula%3B%20KF%29%20is%20used%20to%20treat%20patients%20with%20refractory%20epilepsy.%20We%20investigated%20the%20effect%20of%20KF%20on%20cancer%20and%20cancer%20cachexia%20in%20colon%20tumor-bearing%20mice.%20Mice%20were%20randomized%20into%20normal%20%28NR%29%2C%20tumor-bearing%20%28TB%29%2C%20and%20ketogenic%20formula%20%28KF%29%20groups.%20Colon%2026%20cells%20were%20inoculated%20subcutaneously%20into%20TB%20and%20KF%20mice.%20The%20NR%20and%20TB%20groups%20received%20a%20standard%20diet%2C%20and%20the%20KF%20mice%20received%20KF%20ad%20libitum.%20KF%20mice%20preserved%20their%20body%2C%20muscle%2C%20and%20carcass%20weights.%20Tumor%20weight%20and%20plasma%20IL-6%20levels%20were%20signi%5Cufb01cantly%20lower%20in%20KF%20mice%20than%20in%20TB%20mice.%20In%20the%20KF%20group%2C%20energy%20intake%20was%20signi%5Cufb01cantly%20higher%20than%20that%20in%20the%20other%20two%20groups.%20Blood%20ketone%20body%20concentrations%20in%20KF%20mice%20were%20signi%5Cufb01cantly%20elevated%2C%20and%20there%20was%20a%20signi%5Cufb01cant%20negative%20correlation%20between%20blood%20ketone%20body%20concentration%20and%20tumor%20weight.%20Therefore%2C%20KF%20may%20suppress%20the%20progression%20of%20cancer%20and%20the%20accompanying%20systemic%20in%5Cufb02ammation%20without%20adverse%20effects%20on%20weight%20gain%2C%20or%20muscle%20mass%2C%20which%20might%20help%20to%20prevent%20cancer%20cachexia.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222018-02-14%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fnu10020206%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222072-6643%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F2072-6643%5C%2F10%5C%2F2%5C%2F206%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A41%3A20Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22CQQ6Y2IM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lv%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-12-11%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLv%20M%2C%20Zhu%20X%2C%20Wang%20H%2C%20et%20al%20%282014%29%20Roles%20of%20Caloric%20Restriction%2C%20Ketogenic%20Diet%20and%20Intermittent%20Fasting%20during%20Initiation%2C%20Progression%20and%20Metastasis%20of%20Cancer%20in%20Animal%20Models%3A%20A%20Systematic%20Review%20and%20Meta-Analysis.%20PLoS%20ONE%209%3Ae115147.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0115147%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0115147%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Roles%20of%20Caloric%20Restriction%2C%20Ketogenic%20Diet%20and%20Intermittent%20Fasting%20during%20Initiation%2C%20Progression%20and%20Metastasis%20of%20Cancer%20in%20Animal%20Models%3A%20A%20Systematic%20Review%20and%20Meta-Analysis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mengmeng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lv%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xingya%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hao%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Feng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Wenxian%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Guan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Guillermo%20L%5Cu00f3pez%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lluch%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Background%3A%20The%20role%20of%20dietary%20restriction%20regimens%20such%20as%20caloric%20restriction%2C%20ketogenic%20diet%20and%20intermittent%20fasting%20in%20development%20of%20cancers%20has%20been%20detected%20via%20abundant%20preclinical%20experiments.%20However%2C%20the%20conclusions%20are%20controversial.%20We%20aim%20to%20review%20the%20relevant%20animal%20studies%20systematically%20and%20provide%20assistance%20for%20further%20clinical%20studies.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-12-11%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0115147%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0115147%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A34%3A06Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GM7HUCJD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Poff%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-06-05%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPoff%20AM%2C%20Ari%20C%2C%20Seyfried%20TN%2C%20D%26%23x2019%3BAgostino%20DP%20%282013%29%20The%20Ketogenic%20Diet%20and%20Hyperbaric%20Oxygen%20Therapy%20Prolong%20Survival%20in%20Mice%20with%20Systemic%20Metastatic%20Cancer.%20PLoS%20ONE%208%3Ae65522.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065522%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065522%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20Ketogenic%20Diet%20and%20Hyperbaric%20Oxygen%20Therapy%20Prolong%20Survival%20in%20Mice%20with%20Systemic%20Metastatic%20Cancer%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Angela%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Poff%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Csilla%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Thomas%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Seyfried%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dominic%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22D%5Cu2019Agostino%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chih-Hsin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tang%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Introduction%3A%20Abnormal%20cancer%20metabolism%20creates%20a%20glycolytic-dependency%20which%20can%20be%20exploited%20by%20lowering%20glucose%20availability%20to%20the%20tumor.%20The%20ketogenic%20diet%20%28KD%29%20is%20a%20low%20carbohydrate%2C%20high%20fat%20diet%20which%20decreases%20blood%20glucose%20and%20elevates%20blood%20ketones%20and%20has%20been%20shown%20to%20slow%20cancer%20progression%20in%20animals%20and%20humans.%20Abnormal%20tumor%20vasculature%20creates%20hypoxic%20pockets%20which%20promote%20cancer%20progression%20and%20further%20increase%20the%20glycolytic-dependency%20of%20cancers.%20Hyperbaric%20oxygen%20therapy%20%28HBO2T%29%20saturates%20tumors%20with%20oxygen%2C%20reversing%20the%20cancer%20promoting%20effects%20of%20tumor%20hypoxia.%20Since%20these%20non-toxic%20therapies%20exploit%20overlapping%20metabolic%20deficiencies%20of%20cancer%2C%20we%20tested%20their%20combined%20effects%20on%20cancer%20progression%20in%20a%20natural%20model%20of%20metastatic%20disease.%5CnMethods%3A%20We%20used%20the%20firefly%20luciferase-tagged%20VM-M3%20mouse%20model%20of%20metastatic%20cancer%20to%20compare%20tumor%20progression%20and%20survival%20in%20mice%20fed%20standard%20or%20KD%20ad%20libitum%20with%20or%20without%20HBO2T%20%282.5%20ATM%20absolute%2C%2090%20min%2C%203x%5C%2Fweek%29.%20Tumor%20growth%20was%20monitored%20by%20in%20vivo%20bioluminescent%20imaging.%5CnResults%3A%20KD%20alone%20significantly%20decreased%20blood%20glucose%2C%20slowed%20tumor%20growth%2C%20and%20increased%20mean%20survival%20time%20by%2056.7%25%20in%20mice%20with%20systemic%20metastatic%20cancer.%20While%20HBO2T%20alone%20did%20not%20influence%20cancer%20progression%2C%20combining%20the%20KD%20with%20HBO2T%20elicited%20a%20significant%20decrease%20in%20blood%20glucose%2C%20tumor%20growth%20rate%2C%20and%2077.9%25%20increase%20in%20mean%20survival%20time%20compared%20to%20controls.%5CnConclusions%3A%20KD%20and%20HBO2T%20produce%20significant%20anti-cancer%20effects%20when%20combined%20in%20a%20natural%20model%20of%20systemic%20metastatic%20cancer.%20Our%20evidence%20suggests%20that%20these%20therapies%20should%20be%20further%20investigated%20as%20potential%20non-toxic%20treatments%20or%20adjuvant%20therapies%20to%20standard%20care%20for%20patients%20with%20systemic%20metastatic%20disease.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-6-5%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065522%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065522%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A29%3A05Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22SWT7IIDA%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Poff%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222019%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPoff%20A%2C%20Koutnik%20AP%2C%20Egan%20KM%2C%20et%20al%20%282019%29%20Targeting%20the%20Warburg%20effect%20for%20cancer%20treatment%3A%20Ketogenic%20diets%20for%20management%20of%20glioma.%20Seminars%20in%20Cancer%20Biology%2056%3A135%26%23x2013%3B148.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.semcancer.2017.12.011%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.semcancer.2017.12.011%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Targeting%20the%20Warburg%20effect%20for%20cancer%20treatment%3A%20Ketogenic%20diets%20for%20management%20of%20glioma%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Angela%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Poff%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrew%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Koutnik%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kathleen%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Egan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Solmaz%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sahebjam%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dominic%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22D%5Cu2019Agostino%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nagi%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kumar%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2206%5C%2F2019%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.semcancer.2017.12.011%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221044579X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS1044579X17301244%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A11%3A01Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GWS8CT5H%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Sremanakova%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BSremanakova%20A%20systematic%20review%20of%20the%20use%20of%20ketogenic%20diets%20in%20adult%20patients%20with%20cancer%20-%20Sremanakova%20-%202018%20-%20Journal%20of%20Human%20Nutrition%20and%20Dietetics%20-%20Wiley%20Online%20Library.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fonlinelibrary.wiley.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fjhn.12587%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fonlinelibrary.wiley.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fjhn.12587%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2019%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20systematic%20review%20of%20the%20use%20of%20ketogenic%20diets%20in%20adult%20patients%20with%20cancer%20-%20Sremanakova%20-%202018%20-%20Journal%20of%20Human%20Nutrition%20and%20Dietetics%20-%20Wiley%20Online%20Library%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sremanakova%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fonlinelibrary.wiley.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fjhn.12587%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A03%3A12Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%224RDMGN6M%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Bettum%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BBettum%20IJ%2C%20Gorad%20SS%2C%20Barkovskaya%20A%2C%20et%20al%20%282015%29%20Metabolic%20reprogramming%20supports%20the%20invasive%20phenotype%20in%20malignant%20melanoma.%20Cancer%20Letters%20366%3A71%26%23x2013%3B83.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.canlet.2015.06.006%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.canlet.2015.06.006%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Metabolic%20reprogramming%20supports%20the%20invasive%20phenotype%20in%20malignant%20melanoma%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ingrid%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bettum%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Saurabh%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gorad%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Barkovskaya%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Solveig%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pettersen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Siver%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moestue%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kotryna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vasiliauskaite%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ellen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tenstad%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tove%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22%5Cu00d8yjord%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22%5Cu00d8ystein%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Risa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vigdis%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nygaard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gunhild%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22M%5Cu00e6landsmo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lina%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Prasmickaite%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Invasiveness%20is%20a%20hallmark%20of%20aggressive%20cancer%20like%20malignant%20melanoma%2C%20and%20factors%20involved%20in%20acquisition%20or%20maintenance%20of%20an%20invasive%20phenotype%20are%20attractive%20targets%20for%20therapy.%20We%20investigated%20melanoma%20phenotype%20modulation%20induced%20by%20the%20metastasis-promoting%20microenvironmental%20protein%20S100A4%2C%20focusing%20on%20the%20relationship%20between%20enhanced%20cellular%20motility%2C%20dedifferentiation%20and%20metabolic%20changes.%20In%20poorly%20motile%2C%20well-differentiated%20Melmet%205%20cells%2C%20S100A4%20stimulated%20migration%2C%20invasion%20and%20simultaneously%20down-regulated%20differentiation%20genes%20and%20modulated%20expression%20of%20metabolism%20genes.%20Metabolic%20studies%20con%5Cufb01rmed%20suppressed%20mitochondrial%20respiration%20and%20activated%20glycolytic%20%5Cufb02ux%20in%20the%20S100A4%20stimulated%20cells%2C%20indicating%20a%20metabolic%20switch%20toward%20aerobic%20glycolysis%2C%20known%20as%20the%20Warburg%20effect.%20Reversal%20of%20the%20glycolytic%20switch%20by%20dichloracetate%20induced%20apoptosis%20and%20reduced%20cell%20growth%2C%20particularly%20in%20the%20S100A4%20stimulated%20cells.%20This%20implies%20that%20cells%20with%20stimulated%20invasiveness%20get%20survival%20bene%5Cufb01t%20from%20the%20glycolytic%20switch%20and%2C%20therefore%2C%20become%20more%20vulnerable%20to%20glycolysis%20inhibition.%20In%20conclusion%2C%20our%20data%20indicate%20that%20transition%20to%20the%20invasive%20phenotype%20in%20melanoma%20involves%20dedifferentiation%20and%20metabolic%20reprogramming%20from%20mitochondrial%20oxidation%20to%20glycolysis%2C%20which%20facilitates%20survival%20of%20the%20invasive%20cancer%20cells.%20Therapeutic%20strategies%20targeting%20the%20metabolic%20reprogramming%20may%20therefore%20be%20effective%20against%20the%20invasive%20phenotype.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2209%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.canlet.2015.06.006%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2203043835%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0304383515003985%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A01%3A54Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22D9QF3U55%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hanahan%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BHanahan%20Hallmarks%20of%20Cancer%3A%20The%20Next%20Generation%3A%20Cell.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-ItemURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.cell.com%5C%2Fcell%5C%2Ffulltext%5C%2FS0092-8674%2811%2900127-9%3F_returnURL%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%252Fretrieve%252Fpii%252FS0092867411001279%253Fshowall%253Dtrue%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.cell.com%5C%2Fcell%5C%2Ffulltext%5C%2FS0092-8674%2811%2900127-9%3F_returnURL%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%252Fretrieve%252Fpii%252FS0092867411001279%253Fshowall%253Dtrue%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B.%20Accessed%2019%20Mar%202020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22webpage%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Hallmarks%20of%20Cancer%3A%20The%20Next%20Generation%3A%20Cell%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanahan%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.cell.com%5C%2Fcell%5C%2Ffulltext%5C%2FS0092-8674%2811%2900127-9%3F_returnURL%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%252Fretrieve%252Fpii%252FS0092867411001279%253Fshowall%253Dtrue%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T16%3A00%3A21Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BT3F4UR4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Warburg%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%221956-02-24%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BWarburg%20O%20%281956%29%20On%20the%20Origin%20of%20Cancer%20Cells.%20Science%20123%3A309%26%23x2013%3B314.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.123.3191.309%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.123.3191.309%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22On%20the%20Origin%20of%20Cancer%20Cells%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Warburg%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Cancer%20cells%20originate%20from%20normal%20body%20cells%20in%20two%20phases.%20The%20first%20phase%20is%20the%20irreversible%20injuring%20of%20respiration.%20Just%20as%20there%20are%20many%20remote%20causes%20of%20plague-heat%2C%20insects%2C%20rats-but%20only%20one%20common%20cause%2C%20the%20plague%20bacillus%2C%20there%20are%20a%20great%20many%20remote%20causes%20of%20cancer-tar%2C%20rays%2C%20arsenic%2C%20pressure%2C%20urethane-but%20there%20is%20only%20one%20common%20cause%20into%20which%20all%20other%20causes%20of%20cancer%20merge%2C%20the%20irreversible%20injuring%20of%20respiration.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%221956-02-24%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1126%5C%2Fscience.123.3191.309%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220036-8075%2C%201095-9203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencemag.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.123.3191.309%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%225NYZ8VT6%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-19T15%3A53%3A30Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22SIDRIKSV%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Van%20Wymelbeke%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%221998-08%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BVan%20Wymelbeke%20V%2C%20Himaya%20A%2C%20Louis-Sylvestre%20J%2C%20Fantino%20M%20%281998%29%20Influence%20of%20medium-chain%20and%20long-chain%20triacylglycerols%20on%20the%20control%20of%20food%20intake%20in%20men.%20Am%20J%20Clin%20Nutr%2068%3A226%26%23x2013%3B234.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fajcn%5C%2F68.2.226%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fajcn%5C%2F68.2.226%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Influence%20of%20medium-chain%20and%20long-chain%20triacylglycerols%20on%20the%20control%20of%20food%20intake%20in%20men%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Van%20Wymelbeke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Himaya%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Louis-Sylvestre%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fantino%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Hunger%20may%20be%20delayed%20and%20food%20intake%20reduced%20under%20metabolic%20conditions%20that%20spare%20carbohydrate%20oxidation%2C%20especially%20during%20oxidation%20of%20medium-chain%20triacylglycerols%20%28MCTs%29%20or%20monounsaturated%20triacylglycerols.%20In%2012%20healthy%2C%20adult%2C%20male%20volunteers%20isolated%20and%20deprived%20of%20any%20time%20cues%2C%20we%20compared%20the%20effects%20of%204%20high-carbohydrate%20breakfasts%20%281670%20kJ%29%20supplemented%20either%20with%20a%20fat%20substitute%20%28Sub%3B%2070%20kJ%29%20or%20with%201460%20kJ%20fat%20as%20monounsaturated%20long-chain%20triacylglycerols%20%28LCT-U%29%2C%20saturated%20long-chain%20triacylglycerols%20%28LCT-S%29%2C%20or%20MCTs.%20In%20the%20first%20session%20we%20investigated%20the%20effects%20of%20these%20breakfasts%20on%20the%20following%20food%20intake%20variables%3A%20hunger%20ratings%20at%20repeated%20intervals%2C%20the%20time%20until%20the%20spontaneous%20request%20for%20the%20next%202%20free-choice%20meals%2C%20and%20the%20amount%20of%20food%20consumed.%20In%20a%20second%20session%20with%20fixed%20lunches%2C%20we%20studied%20the%20effects%20of%20the%20same%20breakfasts%20on%20plasma%20glucose%2C%20insulin%2C%20triacylglycerol%2C%20fatty%20acid%2C%20and%20beta-hydroxybutyrate%20concentrations.%20The%20addition%20of%20any%20of%20the%20fats%20to%20the%20high-carbohydrate%20breakfasts%20did%20not%20alter%20hunger%20ratings%2C%20but%20significantly%20delayed%20the%20request%20for%20lunch%20compared%20with%20the%20low-fat%20breakfast.%20The%20free-choice%20lunch%20eaten%20after%20the%20MCT%20breakfast%20was%20also%20significantly%20smaller.%20Blood%20glucose%20and%20insulin%20concentrations%20were%20lower%20after%20the%203%20fat%20breakfasts%2C%20followed%20by%20larger%20increases%20in%20glucose%20and%20enhanced%20insulin%20responses%2030%20min%20after%20the%20lunch.%20No%20differences%20were%20observed%20between%20the%20LCT-U%20and%20LCT-S%20conditions.%20We%20conclude%20that%20MCTs%20decreased%20food%20intake%20by%20a%20postabsorptive%20mechanism%2C%20although%20the%20exact%20effect%20of%20these%20lipids%20on%20carbohydrate%20oxidation%20will%20require%20further%20studies%20involving%20nutrient%20balance%20measurements.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22Aug%201998%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22eng%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fajcn%5C%2F68.2.226%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220002-9165%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HJKVZCPI%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-17T04%3A38%3A54Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%222KSJLCV8%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hellman%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%221969-11-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BHellman%20DE%2C%20Senior%20B%2C%20Goodman%20HM%20%281969%29%20Anti-lipolytic%20effects%20of%20%26%23x3B2%3B-hydroxybutyrate.%20Metabolism%20-%20Clinical%20and%20Experimental%2018%3A906%26%23x2013%3B915.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2F0026-0495%2869%2990031-6%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2F0026-0495%2869%2990031-6%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Anti-lipolytic%20effects%20of%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dorothea%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hellman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Boris%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Senior%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.%20Maurice%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Goodman%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bh2%26gt%3BAbstract%26lt%3B%5C%2Fh2%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bp%26gt%3BThe%20addition%20of%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20to%20epididymal%20fat%20incubated%20in%20vitro%20reduced%20the%20production%20of%20glycerol%20and%20free%20fatty%20acids.%20Inhibition%20of%20lipolysis%20was%20maximal%20%28%5Cu223c%2030%25%29%20when%20physiologic%20concentrations%20of%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20%280.1%20mg.%5C%2Fml.%29%20were%20added%20to%20tissues%20obtained%20from%20fasting%20rats.%20At%20a%20concentration%20of%2010%20mg.%5C%2Fml.%2C%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20also%20abolished%20lipolysis%20in%20response%20to%200.05%20%5Cu03bcg.%5C%2Fml.%20epinephrine%20and%20severely%20reduced%20the%20lipolytic%20effects%20of%20ACTH%20%281%20%5Cu03bcg.%5C%2Fml.%29%2C%20TSH%20%2825%20mU%5C%2Fml.%29%20and%20glucagon%20%2810%20%5Cu03bcg.%5C%2Fml.%29.%20Increasing%20the%20concentration%20of%20epinephrine%20produced%20a%20progressive%20but%20significantly%20lesser%20lipolytic%20response%20in%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20treated%20%2810%20mg.%5C%2Fml.%29%20than%20in%20control%20tissues.%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%2C%2010%20mg.%5C%2Fml.%2C%20abolished%20the%20lipolytic%20response%20to%20theophylline%20%280.54%20mg.%5C%2Fml.%29%2C%20but%20did%20not%20inhibit%20the%20lipolytic%20response%20to%20exogenous%20cyclic%20adenosine%203%5Cu2032%2C5%5Cu2032-monophosphate%20%28CAMP%29%20in%20the%20presence%20of%20theophylline.%20These%20results%20are%20consistent%20with%20the%20concept%20that%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxbutyrate%20may%20modulate%20the%20production%20of%20fatty%20acids%20during%20fasting%20and%20suggest%20that%20the%20antagonism%20of%20epinephrine-induced%20lipolysis%20may%20result%20from%20inhibition%20of%20CAMP%20formation%20in%20adipose%20tissue.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fp%26gt%3B%22%2C%22date%22%3A%221969%5C%2F11%5C%2F01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22English%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2F0026-0495%2869%2990031-6%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220026-0495%2C%201532-8600%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.metabolismjournal.com%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F0026-0495%2869%2990031-6%5C%2Fabstract%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TPPQF3UK%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-16T09%3A51%3A18Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%225JRYL8UX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Newport%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BNewport%20MT%2C%20VanItallie%20TB%2C%20Kashiwaya%20Y%2C%20et%20al%20%282015%29%20A%20new%20way%20to%20produce%20hyperketonemia%3A%20use%20of%20ketone%20ester%20in%20a%20case%20of%20Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs.%20Alzheimers%20Dement%2011%3A99%26%23x2013%3B103.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jalz.2014.01.006%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jalz.2014.01.006%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20new%20way%20to%20produce%20hyperketonemia%3A%20use%20of%20ketone%20ester%20in%20a%20case%20of%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mary%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Newport%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Theodore%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22VanItallie%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yoshihiro%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kashiwaya%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20Todd%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22King%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Veech%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-1%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jalz.2014.01.006%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221552-5260%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC4300286%5C%2F%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TPPQF3UK%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-16T01%3A51%3A50Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QU6JIB96%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Cavaleri%20and%20Bashar%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222018-04-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bclear%3A%20left%3B%20%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-left-margin%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bfloat%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B1.%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-right-inline%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bmargin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3BCavaleri%20F%2C%20Bashar%20E%20%282018%29%20Potential%20Synergies%20of%20%26%23x3B2%3B-Hydroxybutyrate%20and%20Butyrate%20on%20the%20Modulation%20of%20Metabolism%2C%20Inflammation%2C%20Cognition%2C%20and%20General%20Health.%20J%20Nutr%20Metab%202018%3A.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1155%5C%2F2018%5C%2F7195760%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1155%5C%2F2018%5C%2F7195760%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Potential%20Synergies%20of%20%5Cu03b2-Hydroxybutyrate%20and%20Butyrate%20on%20the%20Modulation%20of%20Metabolism%2C%20Inflammation%2C%20Cognition%2C%20and%20General%20Health%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Franco%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cavaleri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Emran%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bashar%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20low-carbohydrate%20high-fat%20diet%20%28LCHFD%29%2C%20also%20known%20as%20the%20ketogenic%20diet%2C%20has%20cycled%20in%20and%20out%20of%20popularity%20for%20decades%20as%20a%20therapeutic%20program%20to%20treat%20metabolic%20syndrome%2C%20weight%20mismanagement%2C%20and%20drug-resistant%20disorders%20as%20complex%20as%20epilepsy%2C%20cancer%2C%20dementia%2C%20and%20depression.%20Despite%20the%20benefits%20of%20this%20diet%2C%20health%20care%20professionals%20still%20question%20its%20safety%20due%20to%20the%20elevated%20serum%20ketones%20it%20induces%20and%20the%20limited%20dietary%20fiber.%20To%20compound%20the%20controversy%2C%20patient%20compliance%20with%20the%20program%20is%20poor%20due%20to%20the%20restrictive%20nature%20of%20the%20diet%20and%20symptoms%20related%20to%20energy%20deficit%20and%20gastrointestinal%20adversity%20during%20the%20introductory%20and%20energy%20substrate%20transition%20phase%20of%20the%20diet.%20The%20studies%20presented%20here%20demonstrate%20safety%20and%20efficacy%20of%20the%20diet%20including%20the%20scientific%20support%20and%20rationale%20for%20the%20administration%20of%20exogenous%20ketone%20bodies%20and%20ketone%20sources%20as%20a%20complement%20to%20the%20restrictive%20dietary%20protocol%20or%20as%20an%20alternative%20to%20the%20diet.%20This%20review%20also%20highlights%20the%20synergy%20provided%20by%20exogenous%20ketone%2C%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20%28BHB%29%2C%20accompanied%20by%20the%20short%20chain%20fatty%20acid%2C%20butyrate%20%28BA%29%20in%20the%20context%20of%20cellular%20and%20physiological%20outcomes.%20More%20work%20is%20needed%20to%20unveil%20the%20molecular%20mechanisms%20by%20which%20this%20program%20provides%20health%20benefits.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222018-4-1%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1155%5C%2F2018%5C%2F7195760%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222090-0724%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC5902005%5C%2F%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TPPQF3UK%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-03-16T01%3A37%3A17Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
1.
Dietze G, Wicklmayr M, Grunst J, Mehnert H (1976) [The anti-ketogenic effect of fructose]. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med 82 Pt 1:767–769
1.
Lee BM, Wolever TM (1998) Effect of glucose, sucrose and fructose on plasma glucose and insulin responses in normal humans: comparison with white bread. Eur J Clin Nutr 52:924–928.
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600666
1.
Pawlosky RJ, Kashiwaya Y, King MT, Veech RL (2020) A Dietary Ketone Ester Normalizes Abnormal Behavior in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. IJMS 21:1044.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031044
1.
Poulain M, Pes GM, Grasland C, et al (2004) Identification of a geographic area characterized by extreme longevity in the Sardinia island: the AKEA study. Experimental Gerontology 39:1423–1429.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2004.06.016
1.
Esposito K, Chiodini P, Colao A, et al (2012) Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 35:2402–2411.
https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-0336
1.
Seeman TE, Crimmins E, Huang M-H, et al (2004) Cumulative biological risk and socio-economic differences in mortality: MacArthur Studies of Successful Aging. Social Science & Medicine 58:1985–1997.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(03)00402-7
1.
Pinquart M, Sörensen S (2000) Influences of socioeconomic status, social network, and competence on subjective well-being in later life: A meta-analysis. Psychology and Aging 15:187–224.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0882-7974.15.2.187
1.
Lemaître J-F, Ronget V, Tidière M, et al (2020) Sex differences in adult lifespan and aging rates of mortality across wild mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1911999117
1.
Madsen EL, Rissanen A, Bruun JM, et al (2008) Weight loss larger than 10% is needed for general improvement of levels of circulating adiponectin and markers of inflammation in obese subjects: a 3-year weight loss study. European Journal of Endocrinology 158:179–187.
https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-07-0721
1.
Nguyen NT, Nguyen X-MT, Wooldridge JB, et al (2010) Association of obesity with risk of coronary heart disease: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2006. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases 6:465–469.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2010.02.038
1.
Partsalaki I, Karvela A, Spiliotis BE (2012) Metabolic impact of a ketogenic diet compared to a hypocaloric diet in obese children and adolescents. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 25:697–704.
https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2012-0131
1.
Kosinski C, Jornayvaz F (2017) Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients 9:517.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050517
1.
Włodarek D (2019) Role of Ketogenic Diets in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease). Nutrients 11:169.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010169
1.
Fine E Targeting insulin inhibition as a metabolic therapy in advanced cancer: a pilot safety and feasibility dietary trial in 10 patients. - PubMed - NCBI.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22840388. Accessed 19 Mar 2020
1.
Kentaro Nakamura, Hidekazu Tonouchi, Akina Sasayama, Kinya Ashida (2018) A Ketogenic Formula Prevents Tumor Progression and Cancer Cachexia by Attenuating Systemic Inflammation in Colon 26 Tumor-Bearing Mice. Nutrients 10:206.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020206
1.
Lv M, Zhu X, Wang H, et al (2014) Roles of Caloric Restriction, Ketogenic Diet and Intermittent Fasting during Initiation, Progression and Metastasis of Cancer in Animal Models: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 9:e115147.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115147
1.
Poff AM, Ari C, Seyfried TN, D’Agostino DP (2013) The Ketogenic Diet and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Prolong Survival in Mice with Systemic Metastatic Cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e65522.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065522
1.
Van Wymelbeke V, Himaya A, Louis-Sylvestre J, Fantino M (1998) Influence of medium-chain and long-chain triacylglycerols on the control of food intake in men. Am J Clin Nutr 68:226–234.
https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/68.2.226
1.
Cavaleri F, Bashar E (2018) Potential Synergies of β-Hydroxybutyrate and Butyrate on the Modulation of Metabolism, Inflammation, Cognition, and General Health. J Nutr Metab 2018:.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7195760


